Abstract
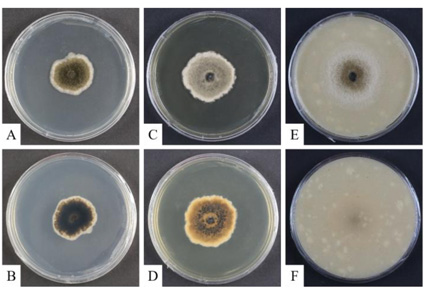
Fungal strains, designated KNU-NL4 and KNU-OL2, belonging to the family Didymellaceae were isolated from a soil sample collected in Miryang, Korea. Phylogenetic analyses based on a concatenated dataset of DNA sequences of ITS regions and partial sequences of ACT, CAL, TEF1-α, and β-TUB genes showed that the isolates reside in a clade together with Boeremia species but occupy the distinct phylogenetic position. Morphologically, the novel strains produce bigger conidiomata (average size 169.8 μm) than the closely related B. rhapontica (126.59 μm) and smaller than the other close neighbor B. coffeae (187.5 μm). Both novel strains also differed from them by smaller colony size and colony color on OA and MEA. The detailed descriptions, illustrations, and discussions regarding the morphological and phylogenetic analyses of the closely related species are provided to support the novelty of the isolated species. The results of phylogenetic analysis and morphological observations indicate that strains KNU-NL4 and KNU-OL2 represent a novel species in the genus Boeremia, for which the name Boeremia parva sp. nov. is proposed.
References
Aveskamp, M.M., Woudenberg, J.H.C., de Gruyter, J., Turco, E., Groenewald, J.Z. & Crous, P.W. (2009) Development of taxon-specific sequence characterized amplified region (SCAR) markers based on actin sequences and DNA amplification fingerprinting (DAF): a case study in the Phoma exigua species complex. Molecular Plant Pathology 10 (3): 403–414. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1364-3703.2009.00540.X
Aveskamp, M.M., de Gruyter, J., Woudenberg, J.H.C., Verkley, G.J.M. & Crous, P.W. (2010) Highlights of the Didymellaceae: A polyphasic approach to characterise Phoma and related pleosporalean genera. Studies in Mycology 65: 1–60. https://doi.org/10.3114/sim.2010.65.01
Berner, D., Cavin, C., Woudenberg, J.H.C., Tunali, B., Büyük, O. & Kansu, B. (2015) Assessment of Boeremia exigua var. rhapontica, as a biological control agent of Russian knapweed (Rhaponticum repens). Biological Control 81: 65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2014.11.009
Betina, V. (1992) Biological effects of the antibiotic brefeldin A (decumbin, cyanein, ascotoxin, synergisidin): a retrospective. Folia Microbiolica 37 (1): 3–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02814572
Boerema, G.H. (1997) Contributions towards a monograph of Phoma (Coelomycetes) – V. Subdivision of the genus in sections. Mycotaxon 64: 321–333.
Boerema, G.H., de Gruyter, J., Noordeloos, M.E. & Hamers, M.E.C. (2004) Phoma identification manual. Differentiation of specific and infra-specific taxa in culture. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, 470 pp.
Bottalico, A., Capasso, R., Evidente, A. & Vurro, M. (1994) Process for the production and purification of cytochalasin B from Phoma exigua var. heteromorpha. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 48 (1): 33–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02825357
Carbone, I. & Kohn, L.M. (1999) A method for designing primer sets for speciation studies in filamentous ascomycetes. Mycologia 91: 553–556. https://doi.org/10.1080/00275514.1999.12061051
Cimmino, A., Andolfi, A., Berestetskiy, A. & Evidente, A. (2008) Production of phytotoxins by Phoma exigua var. exigua, a potential mycoherbicide against perennial thistles. Journal of Agriculture Food Chemistry 56 (15): 6304–6309. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf8004178
Che, Y., Gloer, J.B. & Wicklow, D.T. (2002) Phomadecalins A–D and phomapentenone A: new bioactive metabolites from Phoma sp. NRRL 25697, a fungal colonist of Hypoxylon stromata. Journal of Natural Products 65 (3): 399–402. https://doi.org/10.1021/np010519o
Chen, Q., Zhang, K., Zhang, G.Z. & Cai, L. (2015) A polyphasic approach to characterize two novel species of Phoma (Didymellaceae) from China. Phytotaxa 197 (4): 267–281. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.197.4.4
Chen, Q., Hou, L.W., Duan, W.J. Crous, P.W. & Cai, L. (2017) Didymellaceae revised. Studies in Mycology 87: 105–156. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.simyco.2017.06.002
Damm, U., Cannon, P.F., Woudenberg, J.H.C., Johnston, P.R., Weir, B.S., Tan, Y.P., Shivas, R.G. & Crous, P.W. (2012) The Colletotrichum boninense species complex. Studies in Mycology 73 (1): 1–36. http://dx.doi.org/10.3114/sim0002
de Gruyter, J. & Scheer, P. (1998) Taxonomy and pathogenicity of Phoma exigua var. populi var. nov. causing necrotic bark lesions on poplars. Journal of Phytopathology 146 (8–9): 411–415. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0434.1998.tb04773.x
de Gruyter, J., Boerema, G.H. && Van Der Aa, H.A. (2002) Contributions towards a monograph of Phoma (Coelomycetes) VI–2. Section of Phyllostictoides: Outline of its taxa. Persoonia – Molecular Phylogeny and Evolution of Fungi 18 (1): 1–53.
de Gruyter, J., Aveskamp, M.M., Woudenberg, J.H.C., Verkley, G.J.M., Groenewald, J.Z. & Crous PW. (2009) Molecular phylogeny of Phoma and allied anamorph genera: Towards a reclassification of the Phoma complex. Mycological Research 113: 508–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mycres.2009.01.002
Felsenstein, J. (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. Molecular Biology and Evolution 17: 368–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01734359
Fitch, W.M. (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Systematic Zoology 20 (4): 406–416. https://doi.org/10.2307/2412116
Glass, N.L. & Donaldson, G.C. (1995) Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 61 (4): 1323–1330. http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/aem.61.4.1323-1330.1995
Gorny, A.M., Kikkert, J.R., Dunn, A.R., Dillard, H.R., Smart, C.D. & Pethybridge, S.J. (2015) Tan spot of lima bean caused by Boeremia exigua var. exigua in New York State, USA. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology 37 (4): 523–528. https://doi.org/10.1080/07060661.2015.1105873
Jayasiri, S.C., Hyde, K.D., Jones, E.B., Jeewon, R., Ariyawansa, H.A., Bhat, J.D., Camporesi, E. & Kang, J.C. (2017) Taxonomy and multigene phylogenetic evaluation of novel species in Boeremia and Epicoccum with new records of Ascochyta and Didymella (Didymellaceae). Mycosphere 8 (8): 1080–1101. https://doi.org/10.5943/mycosphere/8/8/9
Jayawardena, R.S., Hyde, K.D., Jeewon, R., Ghobad-Nejhad, M., Wanasinghe, D.N., Liu, N., Phillips, A.J.L., Oliveira-Filho, J.R.C., da Silva, G.A. & Gibertoni, T.B. (2019) One stop shop II: taxonomic update with molecular phylogeny for important phytopathogenic genera: 26-50 (2019). Fungal Diversity 94: 41–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-019-00418-5
Kimura, M. (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. Molecular Biology and Evolution 16 (2): 111–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01731581
Koike, S.T., Subbarao, K.V., Verkley, G.J., Fogle, D. & O?Neil, T.M. (2006) Phoma basal rot of Romaine lettuce in California caused by Phoma exigua: Occurrence, characterization, and control. Plant Disease 90 (10): 1268–1275. https://doi.org/10.1094/PD-90-1268
Kowalski, T., Kraj, W., Bednarz, B. & Rossa, R. (2019) The association of Boeremia lilacis with necrotic lesions on shoots and leaf petioles and its pathogenicity towards Fraxinus excelsior. European Journal of Plant Pathology 154 (4): 961–974. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-019-01715-0
Kumar, S., Stecher, G. & Tamura, K. (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution 33 (7): 1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Larkin, M.A., Blackshields, G., Brown, N.P., Chenna, R., McGettigan, P.A., McWilliam, H., Valentin, F., Wallace, I.M., Wilm, A., Lopez, R., Thompson, J.D., Gibson, T.J. & Higgins, D.G. (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23 (21): 2947–2948. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Marin-Felix, Y., Groenewald, J.Z., Cai, L. Chen, Q., Marincowitz, S., Barnes, I., Bensch, K., Braun, U., Camporesi, E., Damm, U., de Beer, Z.W., Dissanayake, A., Edwards, J., Giraldo, A., Hernández-Restrepo, M., Hyde, K.D., Jayawardena, R.S., Lombard, L., Luangsa-ard, J., McTaggart, A.R., Rossman, A.Y., Sandoval-Denis, M., Shen, M., Shivas, R.G., Tan, Y.P., van der Linde, E.J., Wingfield, M.J., Wood, A.R., Zhang, J.Q., Zhang, Y. & Crous, P.W. (2017) Genera of phytopathogenic fungi: GOPHY 1. Studies in Mycology 86: 99–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simyco.2017.04.002
Monte, E., Bridge, P.D. & Sutton, B.C. (1991) An integrated approach to Phoma systematics. Mycopathologia 115 (2): 89–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00436797
O’Donnell, K. & Cigelnik, E. (1997) Two divergent intragenomic rDNA ITS2 types within a monophyletic lineage of the fungus Fusarium are nonorthologous. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 7 (1): 103–116. https://doi.org/10.1006/mpev.1996.0376
O’Donnell, K., Kistler, H.C., Cigelnik, E. & Ploetz, R.C. (1998) Multiple evolutionary origins of the fungus causing Panama disease of banana: concordant evidence from nuclear and mitochondrial gene genealogies. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 95 (5): 2044–2049. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.5.2044
Park, S., Ten, L., Lee, S.Y., Back, C.G., Lee, J.J., Lee, H.B. & Jung, H.Y. (2017) New recorded species in three genera of the Sordariomycetes in Korea. Mycobiology 45 (2): 64–72. https://doi.org/10.5941/MYCO.2017.45.2.64
Rai, M., Deshmukh, P., Gade, A., Ingle, A., Gyorgy, J. Kovics, G.J. & Irinyi, L. (2009) Phoma Saccardo: distribution, secondary metabolite production and biotechnological applications. Critical Reviews in Microbiology 35 (3): 182–196. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408410902975992
Rai, M., Gade, A., Zimowska, B., Ingle, A.P. & Ingle, P. (2018) Marine-derived phoma-the gold mine of bioactive compounds. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 102 (21): 9053–9066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9329-2
Saitou, N. & Nei, M. (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution 4 (4): 406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Seifert, K.A. (2009) Progress towards DNA barcoding of fungi. Molecular Ecology Resources 9 (Suppl. 1): 83–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02635.x
Singh, S.B., Zink, D.L., Goetz, M.A., Dombrowski, A.W., Polishook, J.D. & Hazuda, D.J. (1998) Equisetin and a novel opposite stereochemical homolog Phomasetin, two fungal metabolites as inhibitors of HIV-1 integrase. Tetrahedron 39 (16): 2243–2246. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(98)00269-X
Stewart, R.B. (1957) Leaf blight and stem dieback of coffee caused by an undescribed species of Ascochyta. Mycologia 49 (3): 430–433. https://doi.org/10.1080/00275514.1957.12024659
Wang, L.W., Xu, B.G., Wang, J.Y., Su, Z.Z., Lin, F.C., Zhang, C.L. & Kubicek, C.P. (2012) Bioactive metabolites from Phoma species, an endophytic fungus from the Chinese medicinal plant Arisaema erubescens. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 93 (3): 1231–1239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3472-3
White, T.J., Bruns, T., Lee, S. & Taylor, J. (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J. & White, T.J. (Eds.) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego (CA), pp. 315–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-372180-8.50042-1