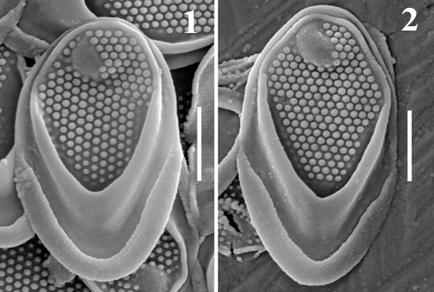
Abstract
This study, conducted in a tropical region, investigates species from the section Papillosae that are morphologically similar to M. furtiva and M. kalinae, using electron microscopy and molecular data. Phylogenetic analysis of three algal cultures resolved a distinct clade, separate from M. furtiva and M. kalinae, in trees based on both SSU rDNA + rbcL cpDNA and ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 rDNA datasets. Based on these results, a new species, Mallomonas imitans sp. nov., is described. This paper discusses the morphological differences between the new species and other Mallomonas taxa within the section Papillosae. The distribution of Mallomonas imitans sp. nov. appears to be restricted, as it has been found in only three localities in Vietnam.
References
- Andersen, R.A. (2005) Algal Culturing Techniques. Elsevier Academic Press, Oxford, 589 pp.
- Asmund, B. & Kristiansen, J. (1986) The genus Mallomonas (Chrysophyceae). A taxonomic survey based on the ultrastructure of silica scales and bristles. Opera Botanica 85: 1–128.
- Belevich, T.A., Ilyash, L.V., Milyutina, I.A., Logacheva, M.D., Goryunov, D.V. & Troitsky, A.V. (2015) Metagenomic analyses of White Sea picoalgae: first data. Biochemistry (Moscow) 80: 1514–1521. https://doi.org/ 10.1134/S0006297915110140
- Bradley, D.E. (1964) A study of the Mallomonas, Synura and Chrysosphaerella of Northern Iceland. Journal of General Microbiology 37: 321–33. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-37-3-321.
- Bradley, D.E. (1966) Observations on some Chrysomonads from Scotland. The Journal of Protozoology 13 (1): 143–154.
- Chernomor, O., von Haeseler, A. & Minh, B.Q. (2016) Terrace aware data structure for phylogenomic inference from supermatrices. Syst. Biol. 65: 997–1008. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syw037
- Choi, B., Son, M., Kim, J.I. & Shin, W. (2013) Taxonomy and phylogeny of the genus Cryptomonas (Cryptophyceae, Cryptophyta) from Korea. Algae 28 (4): 307–330. https://doi.org/10.4490/algae.2013.28.4.307
- Darriba, D., Taboada, G.L., Doallo, R. & Posada, D. (2012) jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nature Methods 9 (8): 1–772. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2109
- Daugbjerg, N. & Andersen, R.A. (1997) Phylogenetic analysis of the rbcL sequences from haptophytes and heterokont algae suggest their chloroplasts are unrelated. Molecular Biology and Evolution 14 (12): 1242–1251. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a025733
- De Saedeleer, H. (1929) Notules systématiques. VI. Physomonas. Annales de Protistologie 2: 177–178.
- Duff, K.E., Zeeb, B.A. & Smol, J.P. (1995) Altas of Chrysophycean Cysts. Dordrecht, Netherlands. 189 pp. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-0809-8
- Dürrschmidt, M. (1983) Three new species of Mallomonas (Chrysophyceae, Mallomonadaceae) from Lake Lanalhue, Chile. Nordic Journal of Botany 3 (3): 423–430.
- Dürrschmidt, M. & Croome, R. (1985) Mallomonadaceae (Chrysophyceae) from Malaysia and Australia. Nordic Journal of Botany 5: 285–298. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1756-1051.1985.tb01657.x
- Gusev, E.S. (2013) Studies on synurophycean algae from mangrove wetlands (Vietnam). Nova Hedwigia, Beihefte 142: 87–98.
- Gusev, E. & Martynenko, N. (2022) Diversity of Silica‐Scaled Chrysophytes in Central Vietnam. Water 14: 1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010065
- Gusev, E.S., Doan-Nhu, H. & Nguyen-Ngoc, L. (2017) Silica-scaled chrysophytes from Cat Tien National Park (Dong Nai Province, Viet Nam). Nova Hedwigia 105: 347–364. https://doi.org/10.1127/nova_hedwigia/2017/0416
- Gusev, E., Shkurina, N. & Huan, P.T. (2023a). Mallomonas acidophila sp. nov. (Synurales, Chrysophyceae) - a new species from the tropics with morphological features of fossil taxa. Phytotaxa 620 (2): 157–166.
- Gusev, E.S., Čertnerová, D., Škaloudová, M. & Škaloud, P. (2018) Exploring cryptic diversity and distribution patterns in the Mallomonas kalinae/rasilis species complex with a description of a new taxon – Mallomonas furtiva sp. nov. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology 65 (1): 38–47. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12427
- Gusev, E.S., Doan-Nhu, H., Nguyen-Ngoc, L. & D.A. Kapustin (2016). Two new species of the genus Mallomonas from the Cat Tien National Park (Viet Nam): Mallomonas distinguenda and Mallomonas skvortsovii. Phytotaxa 273 (1): 59–64. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.273.1.6
- Gusev, E.S., Shkurina, N.A., Tran, H. &. Martynenko, N.A. (2025) Revision of the Mallomonas splendens species clade (Chrysophyceae, Synurales) based on morphological and molecular data. Phytotaxa 708 (3): 241–259. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.708.3.1
- Gusev, E.S., Doan-Nhu, H., Nguyen-Ngoc, L., Guseva, E.E. & Luom, P.T. (2019) Silica-scaled chrysophytes from Cam Ranh Peninsula (Khanh Hoa Province, Vietnam). Nova Hedwigia Beiheft 148: 63–76. https://doi.org/10.1127/nova-suppl/2019/077
- Gusev, E.S., Safronova, T.V., Podunay, Y.А., Tran, H. & Martynenko, N.A. (2024) Hidden diversity in the Mallomonas pseudomatvienkoae species complex (Synurales, Chrysophyceae) and description of two new species. Phycologia 63 (6): 544–557. https://doi.org/10.1080/00318884.2024.2430034
- Gusev, E., Martynenko, N., Shkurina, N., Huan, P.T., Dien, T.D. & Thanh, N.T.H. (2023b) An annotated checklist of algae from the order Synurales (Chrysophyceae) of Viet Nam. Diversity 15 (2): 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020183
- Hamby, R.K., Sims, L., Issel, L. & Zimmer, E. (1988) Direct ribosomal RNA sequencing: optimization of extraction and sequencing methods for work with higher plants. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter 6: 175–192.
- Harris, K. & Bradley, D.E. (1956) An examination of the scales and bristles of Mallomonas in the electron microscope using carbon replicas. Journal of the Royal Microscopical Society 76 (1–2): 37–46.
- Ignatenko, M., Gusev, E. & Yatsenko-Stepanova, T. (2023) Diversity of Silica-Scaled Chrysophytes in the Steppe Zone of the Southern Urals with a Description of a New Species from the Genus Mallomonas. Life 13 (11): 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13112214
- Jo, B.Y., Shin, W., Kim, H.S., Siver, P.A. & Andersen, R.A. (2013) Phylogeny of the genus Mallomonas (Synurophyceae) and descriptions of five new species on the basis of morphological evidence. Phycologia 52: 266–278. https://doi.org/10.2216/12-107.1
- Jo, B.Y., Kim, J.I., Škaloud, P., Siver, P.A. & Shin, W. (2016) Multigene phylogeny of Synura (Synurophyceae) and descriptions of four new species based on morphological and DNA evidence. European Journal of Phycology 51 (4): 413–430.
- Katana, A., Kwiatowski, J., Spalik, K., Zakryś, B., Szalacha, E. & Szymańska, H. (2001) Phylogenetic position of Koliella (Chlorophyta) as inferred from nuclear and chloroplast small subunit rDNA. Journal of Phycology 37 (3): 443–451. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1529-8817.2001.037003443.x
- Katoh, K., Rozewicki, J. & Yamada, K.D. (2019) MAFFT online service: multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Briefings in bioinformatics 20 (4): 1160–1166. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbx108
- Knotek, P., Pusztai, M., Jadrná, I. & Škaloud, P. (2025) Expanding our knowledge of Synurales (Chrysophyceae) in Florida, United States: Proposing three novel Mallomonas taxa. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology 61: 1206–1222. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpy.70062
- Kristiansen, J. & Preisig, H.R. (2007) Chrysophyte and Haptophyte Algae: 2 Teil/2nd Part: Synurophyceae. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg, 252 pp.
- Kristiansen, J. & Škaloud, P. (2017) Chrysophyta. In: Handbook of the Protists. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing: 331–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28149-0_43
- Kumar, S., Stecher, G., Li, M., Knyaz, C. & Tamura, K. (2018) MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Molecular Biology and Evolution 35: 1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
- Lauterborn, R. (1896) Diagnosen neuer Protozoen aus dem Gebiete des Oberrheins. Zoologischer Anzeiger 19: 14–18.
- McFadden, G.I. & Melkonian, M. (1986) Use of Hepes buffer for microalgal culture media and fixation for electron microscopy. Phycologia 25: 551–557. https://doi.org/10.2216/i0031-8884-25-4-551.1
- Minh, B.Q., Schmidt, H.A., Chernomor, O., Schrempf, D., Woodhams, M.D., von Haeseler, A., Lanfear, R. (2020) IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Molecular Biology and Evolution 37: 1530–1534. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msaa015
- Pang, W. & Wang, Q. (2017) Chrysophycean stomatocysts from the Da Hinggan Mountains. Science Press, Beijing, 253 pp.
- Perty, M. (1852) Zur Kenntniss kleinster Lebensformen nach Bau, Funktionen, Systematik, mit Specialverzeichniss der in der Schweiz beobachteten. Jent & Reinert, Bern, 228 pp.
- Peters, M.C. & Andersen, R.A. (1993) The fine structure and scale formation of Chrysolepidomonas dendrolepidota gen. et sp. nov. (Chrysolepidomonadaceae fam. nov., Chrysophyceae). Journal of Phycology 29: 469–475.
- Péterfi, L.S. & Momeu, L. (1976) Romanian Mallomonas species studies in light and electron microscopes. Nova Hedwigia 27: 353–392.
- Podunay, Y., Martynenko, N., Shkurina, N., Tran, H. & Gusev, E. (2025) Two new Mallomonas species (Synurales, Chrysophyceae) from section Torquatae: Mallomonas sagittifera and Mallomonas trifonovae. Phytotaxa 710 (1): 91–104. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.710.1.5
- Pruesse, E., Peplies, J. & Glöckner, F.O. (2012) SINA: Accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 28: 1823–1829. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts252
- Rezácova, M. (2006) Mallomonas kalinae (Synurophyceae), a new species of alga from northern Bohemia, Czech Republic. Preslia 78: 353–358.
- Ronquist, F. & Huelsenbeck, J.P. (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19: 1572–1574. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg180
- Schmidt-Thomé, P., Nguyen, H., Pham, L., Jarva, J. & Nuottimäki, K. (2015) Climate change adaptation measures in Vietnam. Springer International Publishing, Cham, Switzerland, pp. 79–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12346-2
- Siver, P.A. (1991) The Biology of Mallomonas: Morphology, Taxonomy and Ecology. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, Netherlands, 228 pp. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-3376-0
- Siver, P.A. (2024) Mallomonas gigantica sp. nov., an Eocene synurophyte possessing the largest known siliceous scales. Fottea 24 (2): 261–268. https://doi.org/10.5507/fot.2024.006
- Škaloud, P., Kynčlová, A., Benada, O., Kofroňová, O. & Škaloudová, M. (2012) Toward a revision of the genus Synura, section Petersenianae (Synurophyceae, Heterokontophyta): morphological characterization of six pseudo-cryptic species. Phycologia 51 (3): 303–329. https://doi.org/10.2216/11-20.1
- Škaloud, P., Tučková, K., Čablová, R., Jadrná, I. & Černajová, I. (2025) High-frequency sampling unveils biotic and abiotic drivers of rapid phytoplankton morphological changes. New Phytologist: 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.70534
- Takahashi, K. (1972) Studies on genera Mallomonas and Synura, and other plankton in freshwater with the electron microscope. VIII. On three new species of Chrysophyceae. Botanical Magazine 85: 293–302.
- Wee, J.L., Fasone, L.D., Sattler, A., Starks, W.W. & Hurley, D.L. (2001) ITS/5.8S DNA sequence variation in 15 isolates of Synura petersenii Korshikov (Synurophyceae). Nova Hedwigia Beiheft 122: 245–258.
- Zeeb, B.A. & Smol, J.P. (1993) Chrysophycean stomatocyst flora from Elk Lake, Clearwater County, Minnesota. Canadian Journal of Botany 71: 737–756.