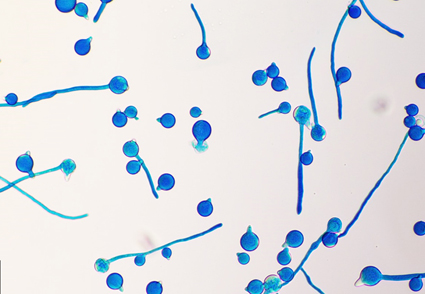
Abstract
The genus Conidiobolus represents fungi of ecological and pathological importance, recently undergoing significant taxonomic revisions driven by molecular advancements. This study describes Conidiobolus srinivasanii sp. nov., a saprobic species isolated from plant litter in Maharashtra, India. Morphological examinations reveal unique features, such as vasiform primary conidiophores, catenate secondary conidia, and multipolar germ tube development, distinguishing it from closely related species. Multigene phylogenetic study (TEF-1α, mtSSU, nucLSU) substantiates its placement within Conidiobolus s.s. while emphasizing genetic divergence from other species. This work integrates morphological observations with genomic data to improve understanding of the taxonomy of this newly described species and underscores the significance of plant litter as a crucial habitat for fungal diversity. These findings aid in the continual refinement of fungal classification and elucidation of the evolutionary complexity of the genus.
References
- Aamir, S., Sutar, S., Singh, S.K. & Baghela, A. (2015) A rapid and efficient method of fungal genomic DNA extraction, suitable for PCR based molecular methods. Plant Pathology & Quarantine 5: 74–81. https://doi.org/10.5943/ppq/5/2/6
- Batko, A. (1964) Notes on entomophthoraceous fungi in Poland Entomophaga. Mémoires hors série 2: 129–131.
- Brefeld, O. (1884) Conidiobolus utriculosus und minor. Untersuchungen aus der Gesammtgebiete der Mykologie 6 (2): 35–78.
- Bruns, T.D., White, T.J. & Taylor, J.W. (1991) Fungal molecular systematics. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 22: 525–564. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.es.22.110191.002521
- Cai, Y., Nie, Y., Zhao, H., Wang, Z., Zhou, Z., Liu, X. & Huang, B. (2021) Azygosporus gen. nov., a synapmorphic clade in the family Ancylistaceae. MycoKeys 85: 161–172. https://doi.org/10.3897/mycokeys.85.73405
- Chakravarti, A. & Mishra, M. (2014) A rare case of rhinofacial zygomycosis due to Conidiobolus infection. An International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Clinics 6: 65–67. https://doi.org/10.5005/jp-journals-10003-1155
- Couch, J.N. (1939) A new Conidiobolus with sexual reproduction. American Journal of Botany 26: 119–130. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1939.tb12878.x
- Drechsler, C. (1952) Widespread distribution of Delacroixia coronata and other saprophytic Entomophthoraceae in plant detritus. Science 115: 575–576. [https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.115.2995.575]
- Drechsler, C. (1953a) Three new species of Conidiobolus isolated from leaf mold. Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences 43: 29–43.
- Drechsler, C. (1953b) Two new species of Conidiobolus occurring in leaf mold. American Journal of Botany 40: 104–115. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1953.tb06458.x
- Drechsler, C. (1954) Two species of Condiobolus with minutely ridged zygospores. American Journal of Botany 41: 567–575. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1954.tb14380.x
- Drechsler, C. (1955a) A small Conidiobolus with globose and with elongated secondary conidia. Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences 45 (4): 114–117.
- Drechsler, C. (1955b) Three new species of Conidiobolus isolated from decaying plant detritus. American Journal of Botany 42: 437–443. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1955.tb11144.x
- Drechsler, C. (1955c) Two new species of Conidiobolus that produce microconidia. American Journal of Botany 42: 793–802. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1955.tb10424.x
- Drechsler, C. (1956) Two new species of Conidiobolus. American Journal of Botany 43: 778–786. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1956.tb11168.x
- Drechsler, C. (1957a) Two small species of Conidiobolus forming lateral zygospores. Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 84: 268–268. https://doi.org/10.2307/2482673
- Drechsler, C. (1957b) A new species of Conidiobolus with distended conidiophores. Sydowia Annales Mycologici 9: 189–192.
- Drechsler, C. (1957c) Two medium-sized species of Conidiobolus occurring in Colorado. Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences 47: 309–315.
- Drechsler, C. (1960) Two new species of Conidiobolus found in plant detritus. American Journal of Botany 47: 368–377. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1960.tb07138.x
- Drechsler, C. (1961) Two species of Conidiobolus often forming zygospores adjacent to antheridium-like distentions. Mycologia 5: 278. https://doi.org/10.2307/3756275
- Drechsler, C. (1962) A small Conidiobolus with resting spores that germinate like zygospores. Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 89: 233–240. https://doi.org/10.2307/2483199
- Drechsler, C. (1965) A robust Conidiobolus with zygospores containing granular parietal protoplasm. Mycologia 57 (6): 913–926. https://doi.org/10.2307/3756891
- Gryganskyi, A.P., Nie, Y., Hajek, A.E., Hodge, K.T., Liu, X.-Y., Aadland, K., Voigt, K., Anishchenko, I.M., Kutovenko, V.B., Kava, L., Vuek, A., Rytas Vilgalys, Huang, B. & Stajich, J.E. (2022) The early terrestrial fungal lineage of Conidiobolus—transition from saprotroph to parasitic lifestyle. Journal of Fungi 8: 789–789. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8080789
- Hawkins, E.C., Grooters, A.M., Cowgill, E.S., Proulx, D., Davainis, G.M., Ruslander, D. & Grindem, C.B. (2006) Treatment of Conidiobolus sp. pneumonia with itraconazole in a dog receiving immunosuppressive therapy. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine 20: 1479–82. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1939-1676.2006.tb00769.x
- Humber, R.A. (1989) Synopsis of a revised classification for the Entomophthorales (Zygomycotina). Mycotaxon 34: 441–460.
- Jaffey, J.A., Hostnik, E.T., Hoffman, A.R., Jay, M., Ferguson, S.H. & Wiederhold, N.P. (2021) Case report: successful management of Conidiobolus lamprauges rhinitis in a dog. Frontiers in Veterinary Science 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2021.633695
- Jensen, A.B., Gargas, A., Eilenberg, J. & Rosendahl, S. (1998) Relationships of the insect-pathogenic order Entomophthorales (Zygomycota, Fungi) based on phylogenetic analyses of nuclear small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences (SSU rDNA). Fungal Genetics and Biology 24: 325–334. https://doi.org/10.1006/fgbi.1998.1063
- Katoh, K. & Standley, D.M. (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30: 772–780. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst010
- King, D.S. (1976) Systematics of Conidiobolus (Entomophthorales) using numerical taxonomy. I. Biology and cluster analysis. Canadian Journal of Botany 54: 45–65. https://doi.org/10.1139/b76-008
- Kornerup, A. & Wanscher, J.H. (1978) Metheun’s handbook of colours, IIIrd Ed. Metheun and Co. Ltd. London, pp. 1–252.
- Larsson, A. (2014) AliView: a fast and lightweight alignment viewer and editor for large datasets. Bioinformatics 30: 3276–3278. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu531
- Mackey, P., Cappe, K.G., Mani, R., Rothenburg, L., Sutton, D.A., Wiederhold, N.P., Lindner, J.R., Ramachandran, A., Wall, C.R. & Snider, T.A. (2015) Disseminated Conidiobolus incongruus in a dog: a case report and literature review. Medical Mycology Case Reports 8: 24–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mmcr.2015.02.005
- Madson, D.M., Loynachan, A.T., Kariyawasam, S. & Opriessnig, T. (2009) Systemic Conidiobolus incongruus infection and hypertrophic osteopathy in a white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation 21: 167–170. https://doi.org/10.1177/104063870902100131
- Martin, G.W. (1925) Morphology of Conidiobolus villosus. Botanical Gazette 80: 311–318. https://doi.org/10.1086/333540
- Nguyen, L.T., Schmidt, H.A., von Haeseler, A. & Minh, B.Q. (2014) IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Molecular Biology and Evolution 32: 268–274. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msu300
- Nie, Y., Yu, C.Z., Liu, X.Y. & Huang, B. (2012) A new species of Conidiobolus (Ancylistaceae) from Anhui, China. Mycotaxon 120: 427–435. https://doi.org/10.5248/120.427
- Nie, Y., Yu, D.S., Wang, C.F., Liu, X.Y. & Huang, B. (2020a) A taxonomic revision of the genus Conidiobolus (Ancylistaceae, Entomophthorales): four clades including three new genera. MycoKeys 66: 55–81. https://doi.org/10.3897/mycokeys.66.46575
- Nie, Y., Cai, Y., Gao, Y., Yu, D.S., Wang, Z.M., Liu, X.Y. & Huang, B. (2020b) Three new species of Conidiobolus sensu stricto from plant debris in eastern China. MycoKeys 73: 133–149. https://doi.org/10.3897/mycokeys.73.56905
- Nie, Y., Wang, Z.M., Liu, X.Y. & Huang, B. (2021) A morphological and molecular survey of Neoconidiobolus reveals a new species and two new combinations. Mycological Progress 20: 1233–1241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-021-01720-w
- Nie, Y., Zhao, H., Wang, Z.M., Zhou, Z.Y., Liu, X.Y. & Huang, B. (2022) Two new species in Capillidium (Ancylistaceae, Entomophthorales) from China, with a proposal for a new combination. MycoKeys 89: 139–153. https://doi.org/10.3897/mycokeys.89.79537
- Nie, Y., Cai, Y., Zhao, H., Zhou, Z., Zhao, C., Liu, X. & Huang, B. (2023) Morphological and phylogenetic analyses reveal two new species in Conidiobolus s.s. (Conidiobolaceae, Entomophthorales) from China. MycoKeys 98: 221–232. https://doi.org/10.3897/mycokeys.98.103603
- Nie, Y., Yin, Y., Zhao, H., Liu, X. & Huang, B. (2024) Unveiling species diversity within the family Conidiobolaceae (Entomophthorales) in China: descriptions of two new species and reassessment of the taxonomic position of Conidiobolus polyspermus. MycoKeys 105: 203–216. https://doi.org/10.3897/mycokeys.105.117871
- Rambaut, A. (2018) FigTree version 1.4.0. Ed.ac.uk. Available from: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed 20 January 2025)
- Ribes, J.A., Vanover-Sams, C.L. & Baker, D.J. (2000) Zygomycetes in human disease. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 13: 236–301. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.13.2.236
- Riet-Correa, F., Dantas, A.F.M., Azevedo, E.O., Simões, S.D.V., Silva, S.M.S., Vilela, R. & Mendoza, L. (2008) Outbreaks of rhinofacial and rhinopharyngeal zygomycosis in sheep in Paraíba, northeastern Brazil. Pesquisa Veterinária Brasileira 28: 29–35. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-736X2008000100005
- Srinivasan, M.C. & Thirumalachar, M.J. (1962a) Studies on species of Conidiobolus from India—II. Sydowia, Annales Mycologici 16: 60–66.
- Srinivasan, M.C. & Thirumalachar, M.J. (1962b) Studies on species of Conidiobolus from India—III. Mycologia 54: 685–693. https://doi.org/10.1080/00275514.1962.12025049
- Srinivasan, M.C. & Thirumalachar, M.J. (1965) Studies on species of Conidiobolus from India—IV. Sydowia 19: 86–91.
- Srinivasan, M.C. & Thirumalachar, M.J. (1967) Evaluation of taxonomic characters in the genus Conidiobolus, with key to known species. Mycologia 59: 698–713. https://doi.org/10.2307/3757098
- Srinivasan, M.C. & Thirumalachar, M.J. (1968) Studies on species of Conidiobolus from India—V. Mycopathologia 36: 341–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02050380
- Taylor, J.W., Jacobson, D.J., Kroken, S., Kasuga, T., Geiser, D.M., Hibbett, D.S. & Fisher, M.C. (2000) Phylogenetic species recognition and species concepts in fungi. Fungal Genetics and Biology 31: 21–32. https://doi.org/10.1006/fgbi.2000.1228
- Vilela, R., Silvana, Riet-Correa, F., Dominguez, E. & Mendoza, L. (2010) Morphologic and phylogenetic characterization of Conidiobolus lamprauges recovered from infected sheep. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 48: 427–432. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.01589-09
- Vilgalys, R. & Hester, M. (1990) Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. Journal of Bacteriology 172: 4238–4246. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.172.8.4238-4246.1990
- Zoller, S., Scheidegger, C. & Sperisen, C. (1999) PCR primers for the amplification of mitochondrial small subunit ribosomal DNA of lichen-forming Ascomycetes. The Lichenologist 31: 511–516. https://doi.org/10.1006/lich.1999.0220