Abstract
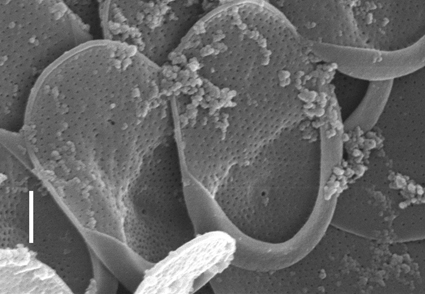
This paper describes a new species of Mallomonas discovered in a swamp area in Russia. The species was identified based on scale morphology, examined using scanning and transmission electron microscopy, and subjected to molecular analysis. The new species, Mallomonas okhapkinii sp. nov., belongs to the section Planae and is most similar in scale and bristle ultrastructure to M. matvienkoae sensu stricto. Phylogenetic analysis, performed using a concatenated dataset of nuclear-encoded small subunit rRNA and plastid-encoded rbcL genes, revealed that the strains of the new species form a distinct clade with high statistical support, closely related to the clade of M. paragrandis and M. sorohexareticulata. This species was found in only one habitat.
References
- Asmund, B. & Kristiansen, J. (1986) The genus Mallomonas (Chrysophyceae). A taxonomic survey based on the ultrastructure of silica scales and bristles. Opera Botanica 85: 1–128.
- Belevich, T.A., Ilyash, L.V., Milyutina, I.A., Logacheva, M.D., Goryunov, D.V. & Troitsky, A.V. (2015) Metagenomic analyses of White Sea picoalgae: first data. Biochemistry 80: 1514–1521. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297915110140
- Čertnerová, D., Čertner, M. & Škaloud, P. (2019) Molecular phylogeny and evolution of phenotype in silica-scaled chrysophyte genus Mallomonas. Journal of Phycology 55: 912–923. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpy.12882
- Choi, B., Son, M., Kim, J.I. & Shin, W. (2013) Taxonomy and phylogeny of the genus Cryptomonas (Cryptophyceae, Cryptophyta) from Korea. Algae 28: 307–330. https://doi.org/10.4490/algae.2013.28.4.307
- Couté, A. & Franceschini, I.M. (1998) Scale-bearing chrysophytes from acid waters of Florianópolis, Santa Catarina Island, South Brazil. Archiv für Hydrobiologie. Supplementband, Algological studies 123: 37–66. https://doi.org/10.1127/algol_stud/88/1998/37
- Cronberg, G. (1989) Stomatocysts of Mallomonas hamata and M. heterospina (Mallomonadaceae, Synurophyceae) from south Swedish lakes. Nordic Journal of Botany 8: 683–692. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1756-1051.1989.tb01745.x
- Darriba, D., Taboada, G.L., Doallo, R. & Posada, D. (2012) jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nature Methods 9: 1–772. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2109
- Daugbjerg, N. & Andersen, R.A. (1997) Phylogenetic analysis of the rbcL sequences from haptophytes and heterokont algae suggest their chloroplasts are unrelated. Molecular Biology and Evolution 14: 1242–1251. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a025733
- Dürrschmidt, M. & Cronberg, G. (1989) Contribution to the knowledge of tropical chrysophytes: Mallomonadaceae and Paraphysomonadaceae from Sri Lanka. Archiv für Hydrobiologie. Supplementband. Monographische Beiträge 82 (1): 15–37.
- Gusev, E.S. (2013) Studies on synurophycean algae from mangrove wetlands (Vietnam). Nova Hedwigia, Beiheft 142: 87–95.
- Gusev, E.S. (2015) A new species of the genus Mallomonas Perty (Synurales, Chrysophyceae) from Vietnam. Algologia 25 (4): 428–438. https://doi.org/10.15407/alg25.04.428
- Gusev, E.S., Doan-Nhu, H. & Nguyen-Ngoc, L. (2017) Silica-scaled Chrysophytes from Cat Tien National Park (Dong Nai Province, Vietnam). Nova Hedwigia 105: 347–364. https://doi.org/10.1127/nova_hedwigia/2017/0416
- Gusev, E.S., Čertnerová, D., Škaloudová, M. & Škaloud, P. (2018) Exploring cryptic diversity and distribution patterns in the Mallomonas kalinae/rasilis species complex with a description of a new taxon—Mallomonas furtiva sp. nov. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology 65 (1): 38–47. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12427
- Gusev, E., Kulizin, P., Guseva, E., Shkurina, N. & Kulikovskiy, M. (2019a) Mallomonas lamii sp. nov. (Synurales, Chrysophyceae), a new species bearing large scales described from the tropics. Phytotaxa 423: 266–272. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.423.4.5
- Gusev, E.S., Perminova, O.S., Guseva, E.E. & Startseva, N.A. (2019b) The genus Mallomonas in small urban rivers in Nizhniy Novgorod (Russia). Nova Hedwigia, Beiheft 148: 77–88. https://doi.org/10.1127/nova-suppl/2019/091
- Gusev, E.S., Doan-Nhu, H., Nguyen-Ngoc, L., Guseva, E.E. & Phan Tan, L. (2019c) Silica-scaled Chrysophytes from Cam Ranh Peninsula (Khanh Hoa Province, Vietnam). Nova Hedwigia, Beiheft 148: 63–76. https://doi.org/10.1127/nova-suppl/2019/077
- Gusev, E., Shkurina, N. & Kulikovskiy, M. (2021a) Mallomonas loricata sp. nov. (Synurales, Chrysophyceae), a new tropical species from section Plantae. Phytotaxa 500 (3): 225–233. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.500.3.6
- Gusev, E., Martynenko, N. & Tran, H. (2021b) Studies on algae from the order Synurales (Chrysophyceae) in Northern Vietnam. Diversity 13, 602: 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13110602
- Gusev, E. & Martynenko, N. (2022) Diversity of silica-scaled Chrysophytes in Central Vietnam. Water 14: 65. [20 pp.] https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010065
- Gusev, E., Kapustin, D., Martynenko, N. & Kulikovskiy, M. (2022a) Diversity of silica-scaled Chrysophytes (Stramenopiles: Chrysophyceae) from Indonesian Papua. Diversity 14: 726. [15 pp.] https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090726
- Gusev, E.S., Guseva, E.E., Dien, T.D. & Kulikovskiy, M.S. (2022b) Flora of silica-scaled Chrysophytes (Chrysophyceae) of two provinces in Southern Viet Nam. Inland Water Biology 15 (3): 205–216. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082922030063
- Gusev, E., Martynenko, N., Kapustin, D., Doan-Nhu, H. & Nguyen-Ngoc, L. (2022c) Diversity of silica-scaled chrysophytes of two tropical islands: Phu Quoc and Con Son (Viet Nam). Life 12: 1611. [19 pp.] https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101611
- Gusev, E., Martynenko, N., Kulizin, P. & Kulikovskiy, M. (2022d) Molecular diversity of the genus Cryptomonas in Russia. European Journal of Phycology 57 (4): 526–550. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670262.2022.2031304
- Gusev, E., Martynenko, N., Shkurina, N., Phan Trong Huan., Tran Duc Dien & Nguyen Thi Hai Thanh (2023) An annotated checklist of algae from the order Synurales (Chrysophyceae) of Viet Nam. Diversity 15: 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020183
- Gusev, E., Shkurina, N. & Martynenko, N. (2024) Phylogenetic position, typification and emended description of Mallomonas matvienkoae (Chrysophyceae, Synurales). Phytotaxa 660: 112–122. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.660.2.2
- Hamby, R.K., Sims, L., Issel, L. & Zimmer, E. (1988) Direct ribosomal RNA sequencing: optimization of extraction and sequencing methods for work with higher plants. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter 6: 175–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02669591
- Hansen, P. (1996) Silica-scaled Chrysophyceae and Synurophyceae from Madagascar. Archiv für Protistenkunde 147: 145–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-9365(96)80030-3
- Jo, B.Y., Shin, W., Boo, S.M., Kim, H.S. & Siver, P.A. (2011) Studies on ultrastructure and three-gene phylogeny of the genus Mallomonas (Synurophyceae). Journal of Phycology 47: 415–425. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8817.2010.00953.x
- Jo, B.Y., Shin, W., Kim, H.S., Siver, P.A. & Andersen, R.A. (2013) Phylogeny of the genus Mallomonas (Synurophyceae) and descriptions of five new species on the basis of morphological evidence. Phycologia 52: 266–278. https://doi.org/10.2216/12-107.1
- Jo, B.Y., Kim, J.I., Škaloud, P., Siver, P.A. & Shin, W. (2016) Multigene phylogeny of Synura (Synurophyceae) and descriptions of four new species based on morphological and DNA evidence. European journal of phycology 51 (4): 413–430. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670262.2016.1201700
- Kapustin, D.A., Gusev, E.S., Lilitskaya, G.G. & Kulikovskiy, M.S. (2020) Silica-scaled chrysophytes from the Ukrainian Polissia. Cryptogamie, Algologie 41 (12): 121–135. https://doi.org/10.5252/cryptogamie-algologie2020v41a12
- Katana, A., Kwiatowski, J., Spalik, K., Zakryś, B., Szalacha, E. & Szymańska, H. (2001) Phylogenetic position of Koliella (Chlorophyta) as inferred from nuclear and chloroplast small subunit rDNA. Journal of Phycology 37: 443–451. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1529-8817.2001.037003443.x
- Katoh, K., Rozewicki, J. & Yamada, K.D. (2019) MAFFT online service: multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Briefings in bioinformatics 20 (4): 1160–1166. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbx108
- Kristiansen, J. & Preisig, H.R. (2007) Chrysophyte and Haptophyte Algae: 2 Teil/2nd Part: Synurophyceae. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg, 252 pp.
- Kumar, S., Stecher, G., Li, M., Knyaz, C. & Tamura, K. (2018) MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Molecular Biology and Evolution 35: 1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
- McFadden, G.I. & Melkonian, M. (1986) Use of Hepes buffer for microalgal culture media and fixation for electron microscopy. Phycologia 25: 551–557. https://doi.org/10.2216/i0031-8884-25-4-551.1
- Momeu, L. & Péterfi, L.S. (1979) Taxonomy of Mallomonas based on the fine structure of scales and bristles. Contributii botanice Cluj-Napoca 30: 13–20.
- Němcová, Y. (2010) Diversity and ecology of silica-scaled chrysophytes (Synurophyceae, Chrysophyceae) in the National Nature Monument Swamp and Břehyňský Pond, Czech Republic. Cryptogamie Algologie 31 (2): 229–243.
- Němcová, Y., Kreidlová, J., Kosová, A. & Neustupa, J. (2012) Lakes and pools of Aquitaine region (France)—a biodiversity hotspot of Synurales in Europe. Nova Hedwigia 95: 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1127/0029-5035/2012/0036
- Nemcova, Y. & Diaz-Pulido, G. (2023) Floristic and ecological insights into silica-scaled chrysophytes in southeastern Queensland, Australia. Plant Systematics and Evolution 309 (6): 43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-023-01881-z
- Perty, M. (1852) Zur Kenntniss Kleinster Lebensformen nach Bau, Funktionen, Systematik, mit Specialverzeichniss der in der Schweiz Beobachteten. Jent & Reinert, Bern, 228 pp.
- Pruesse, E., Peplies, J. & Glöckner, F.O. (2012) SINA: Accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 28: 1823–1829. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts252
- Ronquist, F. & Huelsenbeck, J.P. (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19: 1572–1574. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg180
- Safronova, T.V., Gusev, E.S. & Nguyen, T.L. (2024) Description of the New Species Mallomonas limbata sp. nov. (Synurales, Chrysophyceae) from Water Bodies of Vietnam. Inland Water Biology 17 (1): 82–89. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082924010139
- Saha, L.C. & Wujek, D.E. (1990) Scale-bearing Chrysophytes from Tropical Northeast India. Nordic Journal of Botany 10: 343–355. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1756-1051.1990.tb01777.x
- Siver, P.A. (1991) The Biology of Mallomonas: Morphology, Taxonomy and Ecology. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, Netherlands, 228 pp. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-3376-0
- Siver, P.A. (2024) Mallomonas gigantica sp. nov., an Eocene synurophyte possessing the largest known siliceous scales. Fottea 24: 261–268. https://doi.org/10.5507/fot.2024.006
- Siver, P.A., Jo, B.Y., Kim, J.I., Shin, W., Lott, A.M. & Wolfe, A.P. (2015) Assessing the evolutionary history of the class Synurophyceae (Heterokonta) using molecular, morphometric, and paleobiological approaches. American Journal of Botany 102 (6): 921–941. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1500004
- Škaloud, P., Kynčlová, A., Benada, O., Kofroňová, O. & Škaloudová, M. (2012) Toward a revision of the genus Synura, section
- Petersenianae (Synurophyceae, Heterokontophyta): morphological characterization of six pseudo-cryptic species. Phycologia 51 (3): 303–329. https://doi.org/10.2216/11-20.1
- Takahashi, K. (1972) Studies on genera Mallomonas and Synura, and other plankton in freshwater with the electron microscope. VIII. On three new species of Chrysophyceae. Botanical Magazine 85: 293–302. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02490175
- Takahashi, E. & Hayakawa, T. (1979) The Synuraceae (Chrysophyceae) in Bangladesh. Phykos 18: 129–147.
- Vigna, M.S., Duque, S.R. & Nunez-Avellaneda, M. (2005) Tropical silica-scaled chrysophyte flora (Chrysophyceae and Synurophyceae) from Colombia. Nova Hedwigia 128: 151–166.
- Wee, J.L., Fasone, L.D., Sattler, A., Starks, W.W. & Hurley, D.L. (2001) ITS/5.8S DNA sequence variation in 15 isolates of Synura petersenii Korshikov (Synurophyceae). Nova Hedwigia, Beiheft 122: 245–258.
- Wei, Y.X. & Yuan, X.P. (2001) Studies on silica-scaled chrysophytes from the tropics and subtropics of China. Nova Hedwigia 122: 169–187.
- Wujek, D.E. & Saha, L.C. (1996) Scale-bearing chrysophytes (Chrysophyceae and Synurophyceae) from India. II. Nova Hedwigia Beiheft 112: 367–377.