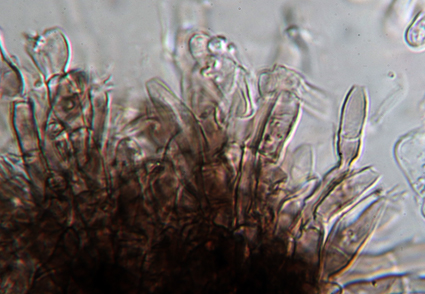
Abstract
Berchemia polyphylla var. leioclada is an important traditional Chinese medicinal plant, it has been proved to produces a variety of unique metabolites, such as glycosides, quinones, lignans, terpenes and flavonoids, with different bioactivities including antioxidant, anti-tumor, anti-diarrheal, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antibacterial activities. Studies showed that endophytic fungi may secrete compounds that are similar to those of the host. Thus, the endophytic fungi of medicinal plants are important medicinal resources and are beneficial to the research and development of natural medicines. Therefore, studying the diversity of endophytic fungi in the medicinal plant of Berchemia polyphylla var. leioclada is of great significance to discovering new drugs. However, the endophytic fungi in Berchemia polyphylla var. leioclada have been poorly studied. This study investigates the endophytic fungi in Berchemia polyphylla var. leioclada from Guizhou Province, China. Two new species Diaporthe berchemiae and Colletotrichum berchemiae are introduced based on morphological characters and multi-locus phylogenetic analysis. This is the first report of endophytic fungi in the medicinal plant Berchemia polyphylla var. leioclada, which enhances our understanding of the endophytic fungi in the medicinal plant Berchemia polyphylla var. leioclada.
References
- Bai, Y., Lin, L., Pan, M. & Fan, X. (2023) Studies of Diaporthe (Diaporthaceae, Diaporthales) species associated with plant cankers in Beijing, China, with three new species described. MycoKeys 98: 59. https://doi.org/10.3897/mycokeys.98.104156
- Baron, N.C. & Rigobelo, E.C. (2022) Endophytic fungi: a tool for plant growth promotion and sustainable agriculture. Mycology 13 (1): 39–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/21501203.2021.1945699
- Bamisile, B.S., Dash, C.K., Akutse, K.S., Keppanan, R. & Wang, L. (2018) Fungal endophytes: beyond herbivore management. Frontiers in Microbiology 9: 544–555 https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00544
- Bhunjun, C.S., Phukhamsakda, C., Jayawardena, R.S., Jeewon, R., Promputtha, I. & Hyde, K.D. (2021) Investigating species boundaries in Colletotrichum. Fungal Diversity 107: 107–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-021-00471-z
- Buchta, V., Nekolová, J., Jirásková, N., Bolehovská, R., Wipler, J. & Hubka, V. (2019) Fungal keratitis caused by Colletotrichum dematium: case study and review. Mycopathologia 184: 441–453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-019-00335-w
- Cai, L., Hyde, K.D., Taylor, P.W.J., Weir, B., Waller, J., Abang, M.M., Zhang, J.Z., Yang, Y.L., Phoulivong, S., Liu, Z.Y. & Shivas, R.G. (2009) A polyphasic approach for studying Colletotrichum. Fungal Diversity 39: 183–204.
- Cai, L., Jeewon, R. & Hyde, K.D. (2005) Phylogenetic evaluation and taxonomic revision of Schizothecium based on ribosomal DNA and protein coding genes. Fungal Diversity 19: 1–21.
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S., Silla-Martínez, J.M. & Gabaldón, T. (2009) trimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 25: 1972–1973. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp348
- Carbone, I. & Kohn, L.M.A (1999) A method for designing primer sets for speciation studies in filamentous ascomycetes. Mycologia 91: 553–556. https://doi.org/10.1080/00275514.1999.12061051
- Chen, L. & Dong, J.X. (2006) Advances in studies on chemical constituents from plants of Berchemia Neck and their bioactivities. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs 37: 627–630. [in Chinese]
- Chepkirui, C. & Stadler, M. (2017) The genus Diaporthe: a rich source of diverse and bioactive metabolites. Mycological Progress 16: 477–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-017-1288-y
- Chung, P.C., Wu, H.Y., Wang, Y.W., Ariyawansa, H.A., Hu, H.P., Hung, T.H., Tzean, S.S. & Chung, C.L. (2020) Diversity and pathogenicity of Colletotrichum species causing strawberry anthracnose in Taiwan and description of a new species, Colletotrichum miaoliense sp. nov. Scientific Reports 10: 14664. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70878-2
- Corda, A.C.I. (1831) Die Pilze Deutschlands. In: Sturm, J. (Ed.) Deutschlands Flora in Abbildungen nach der Natur mit Beschreibungen. Vol. 3. Sturm, Nürnberg, pp. 33–64.
- Crous, P.W., Gams, W., Stalpers, J.A., Robert, V. & Stegehuis, G. (2004) MycoBank: an online initiative to launch mycology into the 21st century. Studies in Mycology 50: 19–22.
- Damm, U., Woudenberg, J.H.C., Cannon, P.F. & Crous, P.W. (2009) Colletotrichum species with curved conidia from herbaceous hosts. Fungal Diversity 39: 45–87.
- de Silva, N.I., Brooks, S., Lumyong, S. & Hyde, K.D. (2019) Use of endophytes as biocontrol agents. Fungal Biology Reviews 33: 133–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbr.2018.10.001
- de Silva, N.I., Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N., Thambugala, K.M., Bhat, D.J., Karunarathna, S.C., Tennakoon, D.S., Phookamsak, R., Jayawardena, R.S., Lumyong, S. & Hyde, K.D. (2021) Morphomolecular taxonomic studies reveal a high number of endophytic fungi from Magnolia candolli and M. garrettii in China and Thailand. Mycosphere 11: 163–237. https://doi.org/10.5943/mycosphere/12/1/3
- Dissanayake, A.J., Chen, Y.Y. & Liu, J.K. (2020) Unravelling Diaporthe species associated with woody hosts from karst formations (Guizhou) in China. Journal of Fungi 6 (4): 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6040251
- Dissanayake, A.J., Phillips, A.J.L., Hyde, K.D., Yan, J.Y. & Li, X.H. (2017) The current status of species in Diaporthe. Mycosphere 8: 1106–1156. https://doi.org/10.5943/mycosphere/8/5/5
- Dissanayake, A.J., Purahong, W., Wubet, T., Hyde, K.D., Zhang, W., Xu, H., Zhang, G., Fu, C., Liu, M., Xing, Q.E., Li, X. & Yan, J. (2018) Direct comparison of culture-dependent and culture-independent molecular approaches reveal the diversity of fungal endophytic communities in stems of grapevine (Vitis vinifera). Fungal Diversity 90: 85–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-018-0399-3
- Farr, D.F., Castlebury, L.A. & Rossman, A.Y. (2002) Morphological and molecular characterization of Phomopsis vaccinii and additional isolates of Phomopsis from blueberry and cranberry in the eastern United States. Mycologia 94: 494–504. https://doi.org/10.1080/15572536.2003.11833214
- Fu, M., Crous, P.W., Bai, Q., Zhang, P.F., Xiang, J., Guo, Y.S., Zhao, F.F., Yang, M.M., Hong, N., Xu, W.X. & Wang, G.P. (2019) Colletotrichum species associated with anthracnose of Pyrus spp. in China. Persoonia: Molecular Phylogeny and Evolution of Fungi 42: 1–35. https://doi.org/10.3767/persoonia.2019.42.01
- Gao, Y.H., Liu, F. & Cai, L. (2016) Unravelling Diaporthe species associated with Camellia. Systematics and Biodiversity 14: 102–117. https://doi.org/10.1080/14772000.2015.1101027
- Garcia-Reyne, A., López-Medrano, F., Morales, J.M., Esteban, C.G., Martín, I., Eraña, I., Meije, Y., Lalueza, A., Alastruey-Izquierdo, A., Rodríguez-Tudela, J.L. & Aguado JM. (2011) Cutaneous infection by Phomopsis longicolla in a renal transplant recipient from Guinea: first report of human infection by this fungus. Transplant Infectious Disease 13: 204–207 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3062.2010.00570.x
- Glass, N.L. & Donaldson, G.C. (1995) Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 61: 1323–1330. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.61.4.1323-1330.1995
- Gomes, R.R., Glienke, C., Videira, S.I.R., Lombard, L., Groenewald, J.Z. & Crous, P.W. (2013) Diaporthe: a genus of endophytic, saprobic and plant pathogenic fungi. Persoonia: Molecular Phylogeny and Evolution of Fungi 31: 1–41. https://doi.org/10.3767/003158513X666844
- Gouda, S., Das, G., Sen, S.K., Shin, H.S. & Patra, J.K. (2016) Endophytes: a treasure house of bioactive compounds of medicinal importance. Frontiers in Microbiology 7: 1538. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01538
- Guarro, J., Svidzinski, T.E., Zaror, L., Forjaz, M.H., Gené, J. & Fischman, O. (1988) Subcutaneous hyalohyphomycosis caused by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 36: 3060–3065. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.36.10.3060-3065.1998
- Guerber, J.C., Liu, B. & Correll, J.C. (2003) Johnston P.R. Characterization of diversity in Colletotrichum acutatum sensu lato by sequence analysis of two gene introns, mtDNA and intron RFLPs, and mating compatibility. Mycologia 95 (5): 872–895. https://doi.org/10.1080/15572536.2004.11833047
- Guo, Y.S., Crous, P.W., Bai, Q., Fu, M., Yang, M.M., Wang, X.H., Du, Y.M., Hong, N., Xu, W.X. & Wang, G.P. (2020) High diversity of Diaporthe species associated with pear shoot canker in China. Persoonia: Molecular Phylogeny and Evolution of Fungi 45: 132–162. https://doi.org/10.3767/persoonia.2020.45.05
- Huang, F., Hou, X., Dewdney, M.M., Fu, Y., Chen, G.Q., Hyde, K.D. & Li, H.Y. (2013) Diaporthe species occurring on citrus in China. Fungal Diversity 61: 237–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-013-0245-6
- Huang, W.Y., Cai, Y., Surveswaran, S., Hyde, K.D., Corke, H. & Sun, M. (2009) Molecular Phylogenetic identification of endophytic fungi isolated from three Artemisia species. Fungal Diversity 36: 69–88.
- Hyde, K.D., Norphanphoun, C., Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N., Bhat, D.J., Jones, E.B.G., Bundhun, D., Chen, Y.J., Bao, D.F., Boonmee, S., Calabon, M.S., Chaiwan, N., Chethana, K.W.T., Dai, D.Q., Dayarathne, M.C., Devadatha, B., Dissanayake, A.J., Dissanayake, L.S., Doilom, M., Dong, W., Fan, X.L., Goonasekara, I.D., Hongsanan, S., Huang, S.K., Jayawardena, R.S., Jeewon, R., Karunarathna, A., Konta, S., Kumar, V., Lin, C.G., Liu, J.K., Liu, N.G., Luangsaard, J., Lumyong, S., Luo, Z.L., Marasinghe, D.S., McKenzie, E.H.C., Niego, A.G.T., Niranjan, M., Perera, R.H., Phukhamsakda, C., Rathnayaka, A.R., Samarakoon, M.C., Samarakoon, S.M.B.C., Sarma, V.V., Senanayake, I.C., Shang, Q.J., Stadler, M., Tibpromma, S., Wanasinghe, D.N., Wei, D.P., Wijayawardene, N.N., Xiao, Y.P., Yang, J., Zeng, X.Y., Zhang, S.N. & Xiang, M.M. Refined families of Sordariomycetes. Mycosphere 11 (1): 305–1059. https://doi.org/10.5943/mycosphere/11/1/
- Hyde, K.D., Xu, J.C., Rapior, S., Jeewon, R., Lumyong, S., Niego, A.G.T., Abeywickrama, P.D., Aluthmuhandiram, J.V.S., Brahamanage, R.S. & Brooks, S. (2019) The amazing potential of fungi: 50 ways we can exploit fungi industrially. Fungal Diversity 97: 1–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-019-00430-9
- Index Fungorum (2023) Available from: http://www.indexfungorum.org/Names/Names.asp (accessed: 21 December 2023).
- Jayasiri, S.C., Hyde, K.D., Ariyawansa, H.A., Bhat, D.J., Buyck, B., Cai, L., Dai, Y.C., Abd-Elsalam, K.A., Ertz, D., Hidayat, I., Jeewon, R., Jones, E.B.G., Bahkali, A.H., Karunarathna, S.C., Liu, J.K., Luangsa-ard, J.J., Lumbsch, H.T., Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N., McKenzie, E.H.C., Moncalvo, J.M., Ghobad-Nejhad, M., Nilsson, H., Pang, K.A., Pereira, O.L., Phillips, A.J.L., Raspé, O., Rollins, A.W., Romero, A.I., Etayo, J., Selçuk, F., Stephenson, S.L., Suetrong, S., Taylor, J.E., Tsui, C.K.M., Vizzini, A., Abdel-Wahab, M.A., Wen, T.C., Boonmee, S., Dai, D.Q., Daranagama, D.A., Dissanayake, A.J., Ekanayaka, A.H., Fryar, S.C., Hongsanan, S., Jayawardena, R.S., Li, W.J., Perera, R.H., Phookamsak, R., de Silva, N.I., Thambugala, K.M., Tian, Q., Wijayawardene, N.N., Zhao, R.L., Zhao, Q., Kang, J.C. & Promputtha, I. (2015) The faces of fungi database: fungal names linked with morphology, phylogeny and human impacts. Fungal Diversity 74: 3–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-020-00439-5
- Katoh, K. & Standleym, D.M. (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30: 772–780. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst010
- Kim, J.W. & Shim, S.H. (2019) The fungus Colletotrichum as a source for bioactive secondary metabolites. Archives of Pharmacal Research 42, 735–753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-019-01142-z
- Kumar, G., Chandra, P. & Choudhary, M. (2017) Endophytic fungi: A potential source of bioactive compounds. Chemical Science Review and Letters 6: 2373–2381.
- Li, G., Kusari, S., Kusari, P., Kayser, O. & Spiteller, M. (2015) Endophytic Diaporthe sp. LG23 produces a potent antibacterial tetracyclic triterpenoid. Journal of Natural Products 78 (8): 2128–2132. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00170
- Liu, F., Cai, L., Crous, P.W. & Damm, U. (2014) The Colletotrichum gigasporum species complex. Persoonia: Molecular Phylogeny and Evolution of Fungi 33: 83–97. https://doi.org/10.3767/003158514X684447
- Liu, F., Ma, Z.Y., Hou, L.W., Diao, Y.Z., Wu, W.P., Damm, U., Song, S. & Cai, L. (2022) Updating species diversity of Colletotrichum, with a phylogenomic overview. Studies in Mycology 101: 1–56. https://doi.org/10.3114/sim.2022.101.01
- Miller, M.A., Pfeiffer, W. & Schwartz, T. (2010) Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In: Proceedings of the 2010 gateway Computing Environments Workshop (gCE), November 2010. New Orleans, Louisiana, pp. 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/GCE.2010.5676129
- Moraga, J., Gomes, W., Pinedo, C., Cantoral, J.M., Hanson, J.R., Carbú, M., Garrido, C., Durán-Patrón, R. & Collado, I.G. (2019) The current status on secondary metabolites produced by plant pathogenic Colletotrichum species. Phytochemistry Reviews 18: 215–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-018-9590-0
- Mostert, L., Crous, P.W., Kang, J.C. & Phillips, A.J.L. (2001) Species of Phomopsis and a Libertella sp. occurring ongrapevines with specific reference to South Africa: morphological, cultural, molecular and pathological characterization. Mycologia 93: 146–167. https://doi.org/10.2307/3761612
- Nitschke, T. (1870) Pyrenomycetes Germanici (2 nd ed.). Eduard Trewendt, Germany, Breslau, pp. 161–320.
- Nylander, J.A.A. (2004) MrModeltest v2. Program Distributed by the Author; Evolutionary Biology Centre, Uppsala University: Uppsala, Sweden.
- O’Donnell, K. & Cigelnik, E. (1997) Two divergent intragenomic rDNA ITS2 types within a monophyletic lineage of the fungus Fusarium are nonorthologous. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 7: 103–116. https://doi.org/10.1006/mpev.1996.0376
- Patchett, A. & Newman, J.A. (2021) Comparison of plant metabolites in root exudates of Lolium perenne infected with different strains of the fungal endophyte Epichlo festucae var. lolii. Journal of Fungi 7: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7020148
- Rannala, B. & Yang, Z. (1996) Probability distribution of molecular evolutionary trees: A new method of phylogenetic inference. Journal of Molecular Evolution 43: 304–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02338839
- Rehner, S.A. & Uecker, F.A. (1994) Nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer phylogeny and host diversity in the coelomycete Phomopsis. Canadian Journal of Botany 72: 1666–1674. https://doi.org/10.1139/b94-204
- Ronquist, F., Teslenko, M., van der Mark, P., Ayres, D.L., Darling, A., Höhna, S., Larget, B., Liu, L., Suchard, M.A. & Huelsenbeck, J.P. (2012) MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology 61: 539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
- Rossman, A.Y., Adams, G.C., Cannon, P.F., Castlebury, L.A., Crous, P.W., Gryzenhout, M., Jaklitsch, W.M., Mejia, L.C., Stoykov, D. & Udayanga, D. (2015) Recommendations of generic names in Diaporthales competing for protection or use. IMA Fungus 6: 145–154. https://doi.org/10.5598/imafungus.2015.06.01.09
- Santos, J.M., Vrandečić, K., Ćosić, J., Duvnjak, T. & Phillips, A.J.L. (2011) Resolving the Diaporthe species occurring on soybean in Croatia. Persoonia: Molecular Phylogeny and Evolution of Fungi 27: 9–19. https://doi.org/10.3767/003158511X603719
- Santos, L., Alves, A. & Alves, R. (2017) Evaluating multi-locus phylogenies for species boundaries determination in the genus Diaporthe. Peer J 5: e3120. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.3120
- Shivaprakash, M.R., Appannanavar, S.B., Dhaliwal, M., Gupta, A., Gupta, S., Gupta, A. & Chakrabarti1, A. (2011) Colletotrichum truncatum: an unusual pathogen causing mycotickeratitis and endophthalmitis. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 49: 2894–2898. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00151-11
- Shuai, L., Liu, H., Liao, L., Lai, T., Lai, Z., Du, X., Duan, Z., Wu, Z. & Luo, T. (2021) Widely targeted metabolic analysis revealed the changed pigmentation and bioactive compounds in the ripening Berchemia floribunda (Wall.) Brongn. fruit. Food Science & Nutrition 9: 1375–1387. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.2093
- Stamatakis, A., Hoover, P. & Rougemont, J. (2008) A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML web servers. Systems Biology 57: 758–771. https://doi.org/10.1080/10635150802429642
- Sun, W., Huang, S., Xia, J., Zhang, X. & Li, Z. (2021) Morphological and molecular identification of Diaporthe species in south-western China, with description of eight new species. MycoKeys 77: 65. https://doi.org/10.3897/mycokeys.77.59852
- Udayanga, D., Liu, X., McKenzie, E.H.C., Chukeatirote, E., Bahkali, A.H.A. & Hyde, K.D. (2011) The genus Phomopsis: biology, applications, species concepts and names of common pathogens. Fungal Diversity 50: 189–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-011-0126-9
- Udayanga, D., Liu, X.Z., Crous, P.W., McKenzie, E.H.C., Chukeatirote, E. & Hyde, K.D. (2012) A multi-locus phylogenetic evaluation of Diaporthe (Phomopsis). Fungal Diversity 56: 157–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-012-0190-9
- van Rensburg, J.C.J., Lamprecht, S.C., Groenewald, J.Z., Castlebury, L.A. & Crous, P.W. (2006) Characterization of Phomopsis spp. associated with die-back of rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) in South Africa. Studies in Mycology 55: 65–74. https://doi.org/10.3114/sim.55.1.65
- Wan, Y., Li, D.W., Si, Y.Z., Li, M., Huang, L. & Zhu, L.H. (2023) Three new species of Diaporthe causing leaf blight on Acer palmatum in China. Plant Disease 107 (3): 849–860. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-06-22-1475-RE
- Wang, Q.T., Liu, F., Hou, C.L. & Cai, L. (2021) Species of Colletotrichum on bamboos from China. Mycologia 113: 450–458. https://doi.org/10.1080/00275514.2020.1837567
- Wehmeyer, L.E. (1993) The genus Diaporthe Nitschke and its segregates. University of Michigan Studies Scientific Series 9: 1–349.
- Weir, B.S., Johnston, P.R. & Damm, U. (2012) The Colletotrichum gloeosporioides species complex. Studies in Mycology 73: 115–180. https://doi.org/10.3114/sim0011
- White, T.J., Bruns, T., Lee, S.J.W.T. & Taylor, J. (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications 18 (1): 315–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-372180-8.50042-1
- Yang, Q., Jiang, N. & Tian, C.M. (2020) Three new Diaporthe species from Shaanxi Province, China. MycoKeys 67: 1–18. https://doi.org/10.3897/mycokeys.67.49483
- Zapata, M., Palma, M.A., Aninat, M.J. & Piontelli, E. (2020) Polyphasic studies of new species of Diaporthe from native forest in Chile, with descriptions of Diaporthe araucanorum sp. nov., Diaporthe foikelawen sp. nov. and Diaporthe patagonica sp. nov. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 70: 3379–3390. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004183
- Zhou, S.X., Zhang, T., Liu, C., Tang, Y.J., Lu, Y.X., Yang, Y.Q., Yu, B. & Shi, K.Z. (2023) Diversity and antibacterial activity and endophytic fungi from Miao medicine Berchemia polyphylla var. leioclada. Guihaia 42: 1236–1243.