Abstract
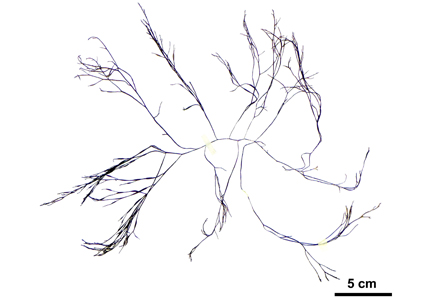
Gongolaria barbata (Sargassaceae, Fucales) is a widespread species for which several infraspecific taxa have been described, indicating its polymorphism. This study contributes to the understanding of the molecular, nomenclatural, morphological and ecological aspects of G. barbata in the Mediterranean and sheds light on the infraspecific diversity and its implications for the taxonomy of this species. Molecular analyses were performed using sequencing of the mitochondrial cox1 gene on both haptophytic and pleustophytic forms from different sites in the Adriatic and Tyrrhenian Seas. Vegetative and reproductive morphology was studied on thalli samples from the Adriatic. Our results showed that there are different morphotypes within G. barbata populations related to specific environmental conditions, suggesting infraspecific variation. In contrast, molecular analyses showed no differences between samples, regardless of whether individuals are growing “attached” to a substrate or “unattached”. We also discussed the taxonomic status and nomenclatural issues related to certain infraspecific taxa previously proposed for G. barbata. In particular, the confusion surrounding Cystoseira aurantia is clarified.
References
- Agardh, C.A. (1820) Species algarum rite cognitae, cum synonymis, differentiis specificis et descriptionibus succinctis. Volumen primum. Pars prima. Ex officina Berlingiana, pp. 1–168. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.45326
- Agardh, J.G. (1842) Algae maris Mediterranei et Adriatici, observationes in diagnosin specierum et dispositionem generum. Apud Fortin, Masson et Cie, pp. 1–164. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.44885
- Alongi, G., Catra, M. & Cormaci, M. (1999) Fenologia morfologica e riproduttiva di Cystoseira elegans Sauvageau (Cystoseiraceae, Phaeophyta). Bollettino dell’Accademia Gioenia di Scienze Naturali di Catania 31: 189–200.
- Amico, V., Giaccone, G., Colombo, P., Colonna, P., Mannino, A.M. & Randazzo, R. (1986 ‘1985’) Un nuovo approccio allo studio della sistematica del genere Cystoseira C. Agardh (Phaeophyta, Fucales). Bollettino dell’Accademia Gioenia di Scienze Naturali di Catania 18: 887–988.
- Battelli, C. & Catra, M. (2021) First report of Cystoseira aurantia (Sargassaceae, Fucophyceae) from the Lagoon of Strunjan (Gulf of Trieste, northern Adriatic). Annales, Series Historia Naturalis 31: 139–146. https://doi.org/10.19233/ASHN.2021.17
- Bouafif, C., Verlaque, M. & Langar, H. (2016) New contribution to the knowledge of the genus Cystoseira C.Agardh in the Mediterranen Sea, with the reinstatemeent of species rank for C. schiffneri Hamel. Cryptogamie Algologie 37: 133–154. https://doi.org/10.7872/crya/v37.iss2.2016.133
- Bruno de Sousa, C., Cox, C.J., Brito, L., Pavao, M.M., Pereira, H., Ferreira, A., Ginja, C., Campino, L., Bermejo, R., Parente, M. & Varela, J. (2019) Improved phylogeny of brown algae Cystoseira (Fucales) from the Atlantic-Mediterranean region based on mitochondrial sequences. PloS ONE 14 e0210143. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0210143
- Cormaci, M., Furnari, G., Catra, M., Alongi, G. & Giaccone, G. (2012) Flora marina bentonica del Mediterraneo: Phaeophyceae. Bollettino dell’Accademia Gioenia di Scienze Naturali di Catania 45: 1–508.
- Cozzi, S., Falconi, C., Comici, C., Čermelj, B., Kovac, N., Turk, V. & Giani, M. (2012) Recent evolution of river discharges in the Gulf of Trieste and their potential response to climate changes and anthropogenic pressure. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 115: 14–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2012.03.005
- Cozzi, S., Reisenhofer, E., Di Monte, L., Cantoni, C. & Adami, G. (2008) Effect of environmental forcing on the fate of nutrients, dissolved organic matter and heavy metals released by a coastal wastewater pipeline. Journal of Chemical Ecology 24: 87–107 https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540801919354
- De Paula, E.J. & De Oliveira, E.C. (1982) Wave exposure and ecotypical differentiation in Sargassum cymosum (Phaeophyta—Fucales). Phycologia 21: 145–153. https://doi.org/10.2216/i0031-8884-21-2-145.1
- Draisma, S.G., Ballesteros, E., Rousseau, F. & Thibaut, T. (2010) DNA sequence data demonstrate the polyphyly of the genus Cystoseira and other Sargassaceae genera (Phaeophyceae). Journal of Phycology 46: 1329–1345. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8817.2010.00891.x
- Edgar, R.C. (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Research 32: 1792–1797. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh340
- Ercegović, A. (1952) Jadranske Cistozire. Sur les Cystoseira adriatiques. Institut za Oceanografiju i Ribarstvo, Split, pp. 1–212
- Falace, A. & Bressan, G. (2006) Seasonal variations of Cystoseira barbata (Stackhouse) C. Agardh frond architecture. Hydrobiologia 555: 193–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-1116-2
- Falace, A. & Zanelli, E. (2006) Studio morfo-funzionale, analisi della complessità e traspianto di habitat forming species (macrophytobenthos). In: Bressan, G. (Ed.) Studio della produttività primaria e della produttività secondaria delle strutture artificiali sommerse poste in prossimità del Dosso di S. Croce Golfo di Trieste alto Adriatico, Trieste. EUT Edizioni Università di Trieste, Italy, pp. 59–72.
- Falace, A., Zanelli, E. & Bressan, G. (2005) Morphological and reproductive phenology of Cystoseira compressa (Esper) Gerloff & Nizamuddin (Fucales, Fucophyceae) in the Gulf of Trieste (North Adriatic Sea). Annales, Series Historia Naturalis 15: 71–78.
- Giaccone, G. & Bruni, A. (1973) Le Cistoseire e la vegetazione sommersa del Mediterraneo. Atti Istituto Veneto di Scienze, Lettere ed arti, Venice 131: 59–103.
- Gómez-Garreta, A., Barceló, M., Gallardo, T., Pérez-Ruzafa, I., Ribera, M. & Rull, J. (2000) Fucales. In: Flora Phycologica Ibérica. Vol. 1. Universidad de Murcia, Servicio de Publicaciones. pp. 99–166.
- Gómez-Garreta, M., Ribera Siguán, M.A. & Seoane Camba, J.A. (1982) Estudio fenológico de varias especies del género Cystoseira en Mallorca. Collectanea botanica 13: 841–855.
- Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (1996–Present) AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication. National University of Ireland, Galway, 2023. Available online: http://www.algaebase.org (accessed: 14 March 2023).
- Hasegawa, M., Kishino, H. & Yano, T. (1985) Dating the human-ape split by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. Journal of Molecular Evolution 22: 160–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02101694
- Hoang, D.T., Chernomor, O., von Haeseler, A., Minh, B.Q. & Vinh, L.S. (2018) UFBoot2: improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Molecular Biololy and Evolution 35: 518–522. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx281
- Hoffmann, L., Renard, R. & Demoulin, V. (1992) Phenology, growth and biomass of Cystoseira balearica in Calvi (Corsica). Marine ecology: progress series 80: 249–254. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps080249
- Kaleb, S., Sánchez de Pedro, R., Bañares-España, E., Alboresi, A., Savonitto, G., Natale, S., Bevilacqua, S. & Falace, A. (2023) Cultivation of Gongolaria barbata (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) with a seaweed-derived biostimulant in order to improve photophysiological fitness and promote fertility to advance the restoration of marine macroalgal forests. Journal of Applied Phycology 35: 2337–2350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-023-02984-3
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S., Minh, B.Q., Wong, T.K.F., von Haeseler, A. & Jermiin, L.S. (2017) ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nature Methods 14: 587–589. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4285
- Kilar, J.A. & Hanisak, M.D. (1989) Phenotypic variability in Sargassum polyceratium (Fucales, Phaeophyta). Phycologia 28: 491–500. https://doi.org/10.2216/i0031-8884-28-4-491.1
- Kumar, S., Stecher, G., Li, M., Knyaz, C. & Tamura, K. (2018) MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Molecular Biology Evolution 35: 1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
- Kützing, F.T. (1843) Phycologia generalis oder Anatomie, Physiologie und Systemkunde der Tange. 1843, Mit 80 farbig gedruckten Tafeln, gezeichnet und gravirt vom Verfasser. pp. [part 1]: [i]–xxxii, [1]–142, [part 2:] 143–458, 1, err.], pls 1–80. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.4746
- Iveša, L., Bilajac, A., Gljušćić, E. & Najdek, M. (2022) Gongolaria barbata forest in the shallow lagoon on the southern Istrian Coast (northern Adriatic Sea). Botanica Marina 65 (4): 255–268. https://doi.org/10.1515/bot-2022-0021
- Lane, C.E., Lindstrom, S. & Saunders, G.W. (2007) A molecular assessment of northeast Pacific Alaria species (Laminariales, Phaeophyceae) with reference to the utility of DNA barcoding. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 44: 634–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2007.03.016
- Lemoine, F., Correia, D., Lefort, V., Doppelt-Azeroual, O., Mareuil, F., Cohen-Boulakia, S. & Gascuel, O. (2019) NGPhylogeny.fr: new generation phylogenetic services for non-specialists. Nucleic Acids Research 47 (W1): W260–W265. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz303
- Letunic, I. & Bork, P. (2021) Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: an online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Research 49 (W1): W293–W296. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab301
- Lüning, K. (1991) Seaweeds: Their Environment, Biogeography, and Ecophysiology. Wiley Interscience publication, John Wiley & Son, Inc., 527 pp.
- Marzocchi, M., Curiel, D., Dri, C. & Scattolin, M. (2003) Fenologia morfologica e riproduttiva di Cystoseira barbata (Stackhouse) C. Agardh var. barbata (Fucales, Fucophyceae) nella laguna di Venezia (Nord Adriatico). Lavori della Società Veneziana di Scienze Naturali 28: 21–23.
- Medrano, A., Hereu, B., Mariani, S., Neiva, J., Pagès-Escolà, M., Paulino, C., la Rovira, G., Serrão, E.A. & Linares, C. (2020) Ecological traits, genetic diversity and regional distribution of the macroalga Treptacantha elegans along the Catalan coast (NW Mediterranean Sea). Scientific Reports 10: 19219. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76066-6
- Minh, B.Q., Schmidt, H.A., Chernomor, O., Schrempf, D., Woodhams, M.D., von Haeseler, A. & Lanfear, R. (2020) IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 37: 1530–1534. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msaa015
- Molinari Novoa, E.A & Guiry, M.D. (2020) Reinstatement of the genera Gongolaria Boehmer and Ericaria Stackhouse (Sargassaceae, Phaeophyceae). Notulae Algarum 172: 1–10.
- Neiva, J., Bermejo, R., Medrano, A., Capdevila, P., Milla-Figueras, D., Afonso, P., Ballesteros, E., Sabour, B., Serio, D., Nóbrega, E., Soares, J., Valdazo, J., Tuya, F., Mulas, M., Israel, Á., Sadogurska, S.S., Guiry, M.D., Pearson, G.A. & Serrão, E.A. (2022) DNA barcoding reveals cryptic diversity, taxonomic conflicts and novel biogeographical insights in Cystoseira s.l. (Phaeophyceae). European Journal of Phycology 58: 351–375. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670262.2022.2126894
- Ogorelec, B., Mišič, M. & Faganeli, J. (0991) Marine geology of the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic): Sedimentological aspects. Marine Geology 99: 79–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-3227(91)90084-H
- Orellana, S., Hernández, M. & Sansón, M. (2019) Diversity of Cystoseira sensu lato (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) in the eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean based on morphological and DNA evidence, including Carpodesmia gen. emend. and Treptacantha gen. emend. European Journal of Phycology 54: 447–465. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670262.2019.1590862
- Orlando-Bonaca, M., Mannoni, P.A., Poloniato, D. & Falace, A. (2013) Assessment of Fucus virsoides distribution in the Gulf of Trieste (Adriatic Sea) and its relation to environmental variables. Botanica Marina 56: 451–459. https://doi.org/10.1515/bot-2013-0027
- Orlando-Bonaca, M., Francé, J., Mavrič, B., Grego, M., Lipej, L., Flander-Putrle, V., Šiško, M. & Falace, A. (2015) A new index (MediSkew) for the assessment of the Cymodocea nodosa (Ucria) Ascherson meadow’s status. Marine Environmental Research 110: 132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2015.08.009
- Orlando-Bonaca, M., Lipej, L. & Orfanidis, S. (2008) Benthic macrophytes as a tool for delineating, monitoring and assessing ecological status: The case of Slovenian coastal waters. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56: 666–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2007.12.018
- Orlando-Bonaca, M., Pitacco, V. & Lipej, L. (2021a) Loss of canopy-forming algal richness and coverage in the northern Adriatic Sea. Ecological Indicators 125: 107501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107501
- Orlando-Bonaca, M., Pitacco, V., Slavinec, P., Šiško, M., Makovec, T. & Falace, A. (2021b) First Restoration Experiment for Gongolaria barbata in Slovenian Coastal Waters. What Can Go Wrong? Plants 10: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020239
- Orlando-Bonaca, M., Savonitto, G., Asnaghi, V., Trkov, D., Pitacco, V., Šiško, M., Makovec, T., Slavinec, P., Lokovšek, A., Ciriaco, S., Chiantore, M., Kaleb, S., Descourvières, E., Srijemsi, M. & Falace, A. (2022) Where and how-new insight for brown algal forest restoration in the Adriatic. Frontiers in Marine Science 9: 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2022.988584
- Pizzuto, F. (1998a) Fenologia morfologica e riproduttiva di Cystoseira crinita Duby (Fucales, Fucophyceae) di Isola delle Correnti (Siracusa, Italia). Bollettino dell’Accademia Gioenia di Scienze Naturali di Catania 30: 129–136.
- Pizzuto, F. (1998b) Fenologia morfologica e riproduttiva di Cystoseira brachycarpa J. Agardh emend. Giaccone (Fucales, Fucophyceae) del litorale catanese (Sicilia orientale). Bollettino dell’Accademia Gioenia di Scienze Naturali di Catania 30: 137–148.
- Ramdani, M., Oufekkir, M.B., El Asri, O., El Khiati, N., Ramdani, M., Denis, F. & Flower, R.J. (2020) First report of Cystoseira aurantia Kützing from the Mediterranean coast of Morocco. Botanica Marina 64: 41–47. https://doi.org/10.1515/bot-2020-0061
- Robvieux, P. (2013) Conservation des populations de Cystoseira en régions Provence-Alpes-Côted’Azur et Corse. Sciences de la Terre. PhD Thesis. Université Nice Sophia Antipolis.
- Ronquist, F., Teslenko, M., van der Mark, P., Ayres, D.L., Darling, A., Höhna, S., Larget, B., Liu, L., Suchard, M.A. & Huelsenbeck, J.P. (2012) MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice Across a Large Model Space. Systematic Biology 61 (3): 539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
- Russell, G. (1978) Environment and form in the discrimination of taxa in brown algae. In: Irvine, D.E.G. & Price, J.H. (Eds.) Modern Approaches to the Taxonomy of Red and Brown Algae. Academic Press, London, pp. 339–369.
- Sadogurska, S.S. (2021) Unattached Cystoseira s.l. in the Black Sea: Taxonomy of Gongolaria barbata f. repens comb. nov. International Journal on Algae 23 (3): 293–304. https://doi.org/10.1615/InterJAlgae.v23.i3.80
- Sadogurska, S.S. (2022) Neprykriplena forma tsystoziry v Chornomu mori: taksonomiya Gongolaria barbata f. repens comb. nov. [Unattached Cystoseira s.l. in the Black Sea: taxonomy of Gongolaria barbata f. repens comb. nov.]. Algologia 31: 150–162. https://doi.org/10.15407/alg31.02.150
- Sadogurska, S.S., Neiva, J., Falace, A., Serrão, E.A. & Israel, A. (2021) The genus Cystoseira s.l. (Ochrophyta, Fucales, Sargassaceae) in the Black Sea: morphological variability and molecular taxonomy of Gongolaria barbata and endemic Ericaria crinita f. bosphorica comb. nov. Phytotaxa 480: 1–21. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.480.1.1
- Sauvageau, C. A (1912) Propos des Cystoseira de Banyuls et de Guéthary. Bulletin de la station biologique d’Arcachon 14: 133–556.
- Savonitto, G., Alongi, G. & Falace, A. (2019) Reproductive phenology, zygote embryology and germling development of the threatened Carpodesmia barbatula (= Cystoseira barbatula) (Fucales, Phaeophyta) towards its possible restoration. Webbia 74: 317–323. https://doi.org/10.1080/00837792.2019.1692594
- Savonitto, G., De La Fuente, G., Tordoni, E., Ciriaco, S., Srijemsi, M., Bacaro, G., Chiantore, M. & Falace, A. (2021) Addressing reproductive stochasticity and grazing impacts in the restoration of a canopy-forming brown alga by implementing mitigation solutions. Aquatic Conservation 31: 1611–1623. https://doi.org/10.1002/aqc.3555
- Schiffner, V. (1933) Meeresalgen aus Sud-Dalmatien, gesammelt von Franz Berger. Österreichische Botanische Zeitschrift 82: 283–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01251322
- Serio, D. (1996a) Fenologia morfologica e riproduttiva di Cystoseira spinosa Sauvageau v. compressa (Ercegovic) Cormaci et al. (Fucales, Fucophyceae). Bollettino dell’Accademia Gioenia di Scienze Naturali di Catania 28: 5–22.
- Serio, D. (1996b) Fenologia morfologica e riproduttiva di Cystoseira zosteroides C. Agardh (Fucales, Fucophyceae). Bollettino dell’Accademia Gioenia di Scienze Naturali di Catania 28: 45–58.
- Silberfeld, T., Leigh, J.W., Verbruggen, H., Cruaud, C., de Reviers, B. & Rousseau, F. (2010) A multi-locus time-calibrated phylogeny of the brown algae (Heterokonta, Ochrophyta, Phaeophyceae): Investigating the evolutionary nature of the “brown algal crown radiation”. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 56 (2): 659–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2010.04.020
- Sideman, E.J. & Mathieson, A.C. (1985) Morphological variation within and between natural populations of non-tide pool Fucus distichus (Phaeophyta) in New England. Journal of Phycology 21: 250–257. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-3646.1985.00250.x
- Silva, P.C., Pedroche, F.F., Chacana, M.E., Aguilar-Rosas, R., Aguilar-Rosas, L.E. & Raum, J. (2004) Geographic correlation of morphological and molecular variation in Silvetia compressa (Fucaceae, Fucales, Phaeophyceae). Phycologia 43: 204–214. https://doi.org/10.2216/i0031-8884-43-2-204.1
- Turland, N.J., Wiersema, J.H., Barrie, F.R., Greuter, W., Hawksworth, D.L., Herendeen, P.S., Knapp, S., Kusber, W.-H., Li, D.-Z., Marhold, K., May, T.W., McNeill, J., Monro, A.M., Prado, J., Price, M.J. & Smith, G.F. (Eds.) (2018) International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (Shenzhen Code) adopted by the Nineteenth International Botanical Congress Shenzhen, China, July 2017. Regnum Vegetabile, Vol. 159. Glashutten: Koeltz Botanical Books. pp. [i]–xxxviii, 1–253. https://doi.org/10.12705/Code.2018
- Woronichin, N.N. (1908) Brown algae (Phaeophyceae) of the Black Sea [In Russian: Бурые водоросли (Phaeophyceae) Черного моря]. Russkii Botanicheskiy Zhurnal [In Russian: Русский Ботанический журнал] 1–2: 19–46; 3–4: 113–138.