Abstract
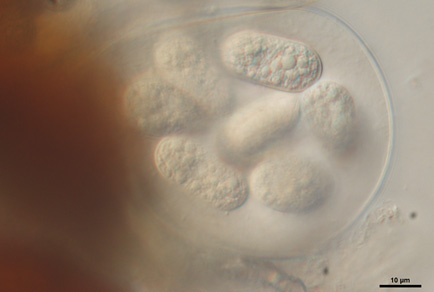
Between 2020 and 2023, Castanopsis sclerophylla, an evergreen broad-leaved tree native to southern China, exhibited powdery mildew symptoms on mature trees in Nanchang, Jiangxi province, with an incidence rate of 50% to 75%. Microscopic examination of the sexual morph revealed that the fungus differed from Erysiphe kissiana by having smaller chasmothecia, and fewer asci and ascospores. These findings were supported by maximum likelihood analysis and Bayesian inference, which showed low bootstrap support and Bayesian posterior probabilities. Based on morphological differences and molecular phylogenetic analysis, we identified this fungus as a new species, Erysiphe jiangxiensis. The pathogenicity of E. jiangxiensis on C. sclerophylla was confirmed using modified Koch’s postulates. The discovery of E. jiangxiensis has significant implications for identifying powdery mildew species on Chinese tanbark-oak and for disease management.
References
- Braun, U. & Takamatsu, S. (2000) Phylogeny of Erysiphe, Microsphaera, Uncinula (Erysipheae) and Cystotheca, Podosphaera, Sphaerotheca (Cystotheceae) inferred from rDNA ITS sequences–some taxonomic consequences. Schlechtendalia 4: 1–33.
- Choi, I.Y., Cheong, S.S., Joa, J.H., Cho, S.E. & Shin, H.D. (2020) First report of powdery mildew caused by Podosphaera xanthii on Sechium edule in Korea. Plant Disease 99: 162. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-10-14-1011-PDN
- Darriba, D., Taboada, G.L., Doallo, R. & Posada, D. (2012) jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and high-performance computing. Nature Methods 9: 772. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2109
- Divarangkoon, R., Meeboon, J., Monkhung, S., To-anun, C. & Takamatsu, S. (2011) Two new species of Erysiphe (Erysiphales, Ascomycota) from Thailand. Mycosphere 2: 231–238.
- Huang, C.C. & Chang, Y. (1998) Fagaceae. In: Huang, C.C. (Ed.) Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae. Vol. 22. Science Press, Beijing, pp. 25–26.
- Katoh, K. & Standley, D.M. (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30: 772–780. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst010
- Meeboon, J., Hidayat, I. & Takamatsu, S. (2012) Erysiphe javanica sp. nov., a new tropical powdery mildew from Indonesia. Mycotaxon 120: 189–194. https://doi.org/10.5248/120.189
- Rambaut, A. (2018) FigTree ver. 1.4.4. Available from: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree (accessed 20 March 2020)
- Ronquist, F., Teslenko, M., Van Der Mark, P., Ayres, D.L., Darling, A., Höhna, S., Larget, B., Liu, L., Suchard, M.A. & Huelsenbeck, J.P. (2012) MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology 61: 539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
- Stamatakis, A. (2014) RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30: 1312–1313. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033
- Takamatsu, S., Braun, U., Limkaisang, S., Kom-Un, S., Sato, Y. & Cunnington, J.H. (2007) Phylogeny and taxonomy of the oak powdery mildew Erysiphe alphitoides sensu lato. Mycological Research 111: 809–826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mycres.2007.05.013
- Takamatsu, S., Siahaan, S.A.S. & Shinoda, T. (2015) Erysiphe kissiana sp. nov.: first finding of sect. Californiomyces in Japan. Mycoscience 56: 512–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.myc.2015.03.002
- Walsh, P.S., Metzger, D.A. & Higuchi, R. (1991) Chelex 100 as a medium for simple extraction of DNA for PCR-based typing from forensic material. Biotechniques 10: 506–513.
- White, T.J., Bruns, T., Lee, S. & Taylor, J. (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J. & White, T.J. (Eds.) PCR protocols: a guide to methods applications. Academic Press, pp. 315–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-372180-8.50042-1