Abstract
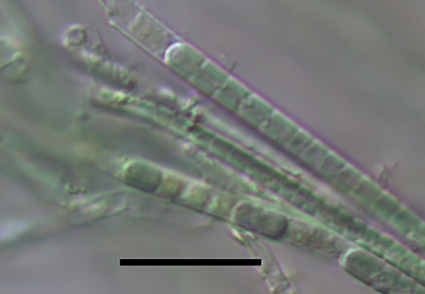
The middle route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project supplies high-quality water to various water treatment plants along its path and increases the diversity of cyanobacteria present in the raw water. A filamentous cyanobacterium Leptodesmis xinxiangensis HNU2023 was successfully isolated from a drinking water plant in Xinxiang, which receives its water supply from this middle route. Morphologically, this strain exhibits similarities to cyanobacterial taxa within the genera Leptodesmis and Phormidesmis. Phylogenetic analysis, based on 16S rRNA gene sequences, indicates that this strain is closely related to Leptodesmis, forming a well-supported clade. The 16S rRNA gene sequences of the strain show between 95.5% and 98% similarity to known Leptodesmis species, suggesting that it represents a new species within this genus. Moreover, the distinctive patterns observed in the D1-D1′ and Box-B helix regions of the 16S–23S rRNA internal transcribed spacer (ITS) secondary structure further confirm that this strain is a novel species. Consequently, the comprehensive analysis of the isolated strain, in conjunction with morphological characteristics, 16S rRNA gene sequencing, and ITS secondary structure, substantiates the classification of Leptodesmis xinxiangensis sp. nov. as a new species within the genus Leptodesmis.
References
- Albertano, P. & Kovacik, L. (1994) Is the genus Leptolyngbya (Cyanophyte) a homogeneous taxon? Archiv für Hydrobiologie-Supplement 105: 37–37. https://doi.org/10.1127/algol_stud/75/1995/37
- Anagnostidis, K. (1985) Modern approach to the classification system of cyanophytes. 1-Introduction. Archiv für Hydrobiologie-Supplement 38–39: 291–302.
- Cai, F., Yu, G. & Li, R. (2022) Description of two new species of Pseudoaliinostoc (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria) from China based on the polyphasic approach. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology 40 (3): 1233–1244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-021-1111-0
- Caires, T.A., Lyra, G.D., Hentschke, G.S., da Silva, A.M.S., de Araujo, V.L., Sant’Anna, C.L. & Nunes, J.M.D. (2018) Polyphasic delimitation of a filamentous marine genus, Capillus gen. nov. (Cyanobacteria, Oscillatoriaceae) with the description of two Brazilian species. Algae 33 (4): 291–304. https://doi.org/10.4490/algae.2018.33.11.25
- Edwards, U., Rogall, T., Blöcker, H., Emde, M. & Böttger, E.C. (1989) Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes. Characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Research 17 (19): 7843–7853. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/17.19.7843
- Elkins, K.M. (2013) Analysis of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequence data using BioEdit. Forensic DNA Biology 129–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-394585-3.00015-8
- Geng, R., Cheng, Y., Chen, S., Zhang, H., Xiao, P., Chen, S., Ma, Z., Han, B. & Li, R. (2024) Maricoleus vaginatus gen. et sp. nov. (Oculatellaceae, Synechococcales), a novel cyanobacterium isolated from a marine ecosystem in China. FOTTEA 24 (1): 27–41. https://doi.org/10.5507/fot.2023.005
- Gkelis, S., Rajaniemi, P., Vardaka, E., Moustaka-Gouni, M., Lanaras, T. & Sivonen, K. (2005) Limnothrix redekei (Van Goor) meffert (Cyanobacteria) strains from lake kastoria, Greece form a separate phylogenetic group. Microbial Ecology 49 (1): 176–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-003-2030-7
- Hoffmann, L., Komárek, J. & Kaštovský, J. (2005) Proposal of cyanobacterial system-2004. Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa 19 (2): 657–660.
- Iteman, I., Rippka, R., Tandeau, de Marsac, N. & Herdman, M. (2000) Comparison of conserved structural and regulatory domains within divergent 16S rRNA-23S rRNA spacer sequences of cyanobacteria. Microbiology (Reading, England) 146 (6): 1275–1286. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-146-6-1275
- Jasser, I., Kostrzewska-Szlakowska, I., Kwiatowski, J., Navruzshoev, D., Suska-Malawska, M. & Khomutovska, N. (2020) Morphological and Molecular Diversity of Benthic Cyanobacteria Communities Versus Environmental Conditions in Shallow, High Mountain Water Bodies in Eastern Pamir Mountains (Tajikistan). Polish Journal of Ecology 67: 286–304. https://doi.org/10.3161/15052249PJE2019.67.4.002
- Komárek, J. (2018) Several problems of the polyphasic approach in the modern cyanobacterial system. Hydrobiologia 811: 7–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3379-9
- Komárek, J. (2005) Cyanoprokaryota 2. Teil/2nd part: Oscillatoriales. Susswasserflora von Mitteleuropa 19: 1–759.
- Komárek, J. (2016) A polyphasic approach for the taxonomy of cyanobacteria: principles and applications. European Journal of Phycology 51 (3): 346–353. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670262.2016.1163738
- Komárek, J., Johansen, J.R., Šmarda, J. & Strunecký, O. (2020) Phylogeny and taxonomy of Synechococcus-like cyanobacteria. Fottea 20 (2): 171–191. https://doi.org/10.5507/fot.2020.006
- Komárek, J., Kaštovský, J., Mareš, J. & Johansen, J.R. (2014) Taxonomic classification of cyanoprokaryotes (cyanobacterial genera) 2014, using a polyphasic approach. Preslia 86 (4): 295–335.
- Ludwig, W., Strunk, O., Klugbauer, S., Klugbauer, N., Weizenegger, M., Neumaier, J., Bachleitner, M. & Schleifer, K.H. (1998) Bacterial phylogeny based on comparative sequence analysis. Electrophoresis 19 (4): 554–568. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.1150190416
- Luz, R., Cordeiro, R., Kaštovský, J., Fonseca, A., Urbatzka, R., Vasconcelos, V. & Gonçalves, V. (2023) Description of Pseudocalidococcus azoricus gen. sp. nov. (Thermosynechococcaceae, Cyanobacteria), a Rare but widely distributed coccoid cyanobacteria. Diversity 15 (12): 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15121157
- Luz, R., Cordeiro, R., Kaštovský, J., Johansen, J.R., Dias, E., Fonseca, A., Urbatzka, R., Vasconcelos, V. & Gonçalves, V. (2023) Description of four new filamentous cyanobacterial taxa from freshwater habitats in the Azores Archipelago. Journal of Phycology 59 (6): 1323–1338. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpy.13396
- Lyons, T., Reinhard, C. & Planavsky, N. (2014) The rise of oxygen in earth’s early ocean and atmosphere. Nature 506: 307–315. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13068
- Mares, J. (2018) Multilocus and SSU rRNA gene phylogenetic analyses of available cyanobacterial genomes, and their relation to the current taxonomic system. Hydrobiologia 811 (1): 19–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3373-2
- Mareš, J., Strunecký, O., Bučinská, L. & Wiedermannová, J. (2019) Evolutionary patterns of thylakoid architecture in cyanobacteria. Frontiers in Microbiology 10: 277. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00277
- Neilan, B.A., Jacobs, D. & Goodman, A.E. (1995) Genetic diversity and phylogeny of toxic cyanobacteria determined by DNA polymorphisms within the phycocyanin locus. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 61 (11): 3875–3883. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.61.11.3875-3883.1995
- Nguyen, L.T., Schmidt, H.A., von Haeseler, A. & Minh, B.Q. (2015) IQTREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Molecular Biology and Evolution 32 (1): 268–274. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msu300
- Page, R.D. (1996) Tree View: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Computer applications in the biosciences : CABIOS 12 (4): 357–358. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/12.4.357
- Panou, M. & Gkelis, S. (2022) Unravelling unknown cyanobacteria diversity linked with HCN production. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 166: 107322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2021.107322
- Perkerson, R.B., Perkerson, E.A. & Casamatta, D.A. (2010) Phylogenetic examination of the cyanobacterial genera Geitlerinema and Limnothrix (Pseudanabaenaceae) using 16S rDNA gene sequence data. Algological Studies 134: 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1127/1864-1318/2010/0134-0001
- Pietrasiak, N., Mühlsteinová, R., Siegesmund, M.A. & Johansen, J.R. (2014) Phylogenetic placement of Symplocastrum (Phormidiaceae, Cyanophyceae) with a new combination S. californicum and two new species: S. flechtnerae and S. torsivum. Phycologia 53 (6): 529–541. https://doi.org/10.2216/14-029.1
- Prihantini, N.B. (2020) Morphological identification, isolation, and culturing of cyanobacteria derived from hot spring of Cisolok and Galunggung Mountain based on enrichment method. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 1442. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1442/1/012069
- Raabová, L., Kováčik, L., Elster, J. & Strunecký, O. (2019) Review of the genus Phormidesmis (Cyanobacteria) based on environmental, morphological, and molecular data with description of a new genus Leptodesmis. Phytotaxa 395 (1): 1–16. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.395.1.1
- Roeselers, G., Norris, T.B., Castenholz, R.W., Rysgaard, S., Glud, R.N., Kühl, M. & Muyzer, G. (2007) Diversity of phototrophic bacteria in microbial mats from Arctic hot springs (Greenland). Environmental microbiology 9 (1): 26–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462–2920.2006.01103.x
- Sánchez-Baracaldo, P., Bianchini, G., Wilson, J.D. & Knoll, A.H. (2022) Cyanobacteria and biogeochemical cycles through earth history. Trends in Microbiology 30 (2): 143–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2021.05.008
- Strunecký, O., Ivanova, A.P. & Mareš, J. (2023) An updated classification of cyanobacterial orders and families based on phylogenomic and polyphasic analysis. Journal of Phycology 59 (1): 12–51. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpy.13304
- Strunecky, O., Raabova, L., Bernardova, A., Ivanova, A.P., Semanova, A., Crossley, J. & Kaftan, D. (2020) Diversity of cyanobacteria at the Alaska North Slope with description of two new genera: Gibliniella and Shackletoniella. FEMS microbiology ecology 96 (3): fiz189. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiz189
- Tamura, K., Stecher, G. & Kumar, S. (2021) MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Molecular Biology and Evolution 38 (7): 3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab120
- Tang, J., Du, L.M., Li, M., Yao, D., Jiang, Y., Waleron, M., Waleron, K. & Daroch, M. (2022) Characterization of a novel hot-spring cyanobacterium Leptodesmis sichuanensis sp. nov. and Genomic Insights of Molecular Adaptations Into Its Habitat. Frontiers in microbiology 12: 739625. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.739625
- Turicchia, S., Ventura, S., Komárková, J. & Komárek, J. (2009) Taxonomic evaluation of cyanobacterial microflora from alkaline marshes of northern Belize. 2. Diversity of oscillatorialean genera. Nova Hedwigia 89: 165–200. https://doi.org/10.1127/0029-5035/2009/0089-0165
- Vaccarino, M.A. & Johansen, J.R. (2012) Brasilonema angustatum sp. nov. (Nostocales), a new filamentous cyanobacterial species from the Hawaiian Islands. Journal of phycology 48 (5): 1178–1186. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8817.2012.01203.x
- Wilmotte, A. (1994) Molecular evolution and taxonomy of the cyanobacteria. In: Bryant, D.A. (Ed.) The Molecular Biology of Cyanobacteria. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp. 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-0227-8
- Whitton, B.A. (2012) Ecology of cyanobacteria II: Their diversity in space and time. Springer, Dordrecht, 760 pp.
- Xiang, C.Y., Gao, F., Jakovlić, I., Lei, H.P., Hu, Y., Zhang, H., Zou, H., Wang, G.T. & Zhang, D. (2023) Using PhyloSuite for molecular phylogeny and tree-based analyses. iMeta 2 (1): e87. https://doi.org/10.1002/imt2.87
- Xie, Y., Zhang, R.Z., Zhang, K.D., Lv, X.J., Zhang, H., Xiao, P., Li, R.H, Cheng, Y. & Geng, R.Z. (2023) Limnoraphis (Oscillatoriales, Cyanobacteria), a bloom-forming genus newly recorded from China. Journal of Henan Normal University (Natural Science Edition) 51 (4): 125–131.
- Zhang, D., Gao, F., Jakovlić , I., Zou, H., Zhang, J., Li, W.X. & Wang, G.T. (2020) PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Molecular ecology resources 20 (1): 348–355. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.13096
- Zhang, X., Xu, J., Dai, J., Zhang, L., Feng, L., Tian, X. & Yang, Q. (2024) Taxonomic, Phylogenomic and Bioactivity Profiling of Novel Phycosphere Bacterium from Model Cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942. Marine Drugs 22 (1): 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010036
- Zhang, Z.C., Li, Z.K., Yin, Y.C., Li, Y., Jia, Y., Chen, M. & Qiu, B.S. (2019) Widespread occurrence and unexpected diversity of red-shifted chlorophyll producing cyanobacteria in humid subtropical forest ecosystems. Environ Microbiol 21 (4): 1497–1510. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.14582