Abstract
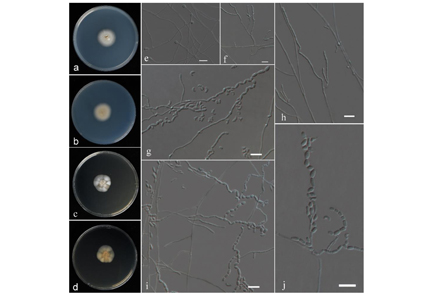
During a survey of keratinolytic fungi in China, a new species, Arthrographis multiformispora was isolated from soil samples. Morphologically, A. multiformispora differs from other species in the genus by the presence of globose or subglobose chlamydospores and cylindrical arthroconidia. Phylogenetically, our four strains were clustered together with high support values and separated from other clades. We provided a description, illustrations, and phylogenetic tree for the new species.
References
Biser, S.A., Perry, H.D., Donnenfeld, E.D., Doshi, S.J. & Chaturvedi, V. (2004) Arthrographis kalrae mimicking acanthamoeba keratitis. Cornea 23: 314–317. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003226-200404000-00018
Boana, P., Arthur, I., Golledge, C. & Ellis, D. (2012) Refractory Arthrographis kalrae native knee joint infection. Medical Mycology Case Reports 1 (1): 112–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mmcr.2012.10.005
Capella-Gutierrez, S., Silla-Martinez, J.M. & Gabaldon, T. (2009) TrimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 25: 1972–1973. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp348
Chen, C.J., Chen, H., Zhang, Y., Thomas, H.R., Frank, M.H., He, Y.H. & Xia, R. (2020) TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Molecular Plant 13 (8): 1194–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Chin-Hong, P.V., Sutton, D.A., Roemer, M., Jacobson, M.A. & Aberg, J.A. (2001) Invasive fungal sinusitis and meningitis due to Arthrographis kalrae in a patient with AIDS. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 39: 804–807. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.39.2.804-807.2001
Giraldo, A., Gené, J., Sutton, D.A., Madrid, H., Cano, J., Crous, P.W. & Guarro, J. (2014) Phylogenetic circumscription of Arthrographis (Eremomycetaceae, Dothideomycetes). Persoonia 32: 102–114. https://doi.org/10.3767/003158514x680207
Hernández-Restrepo, M., Giraldo, A., van Doorn, R., Wingfield, M.J., Groenewald, J.Z., Barreto, R.W., Colmán, A.A., Mansur, P.S.C. & Crous, P.W. (2020) The genera of Fungi – G6: Arthrographis, Kramasamuha, Melnikomyces, Thysanorea, and Verruconis. Fungal Systematics and Evolution 6 (1). https://doi.org/10.3114/fuse.2020.06.01
Kalyaanamoorthy, S., Minh, B.Q., Wong, T.K.F., von Haeseler, A. & Jermiin, L.S. (2017) ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nature Methods 14 (6): 587–589. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4285
Kang, H.J., Sigler, L., Lee, J., Gibas, C.F., Yun, S.H. & Lee, Y.W. (2010) Xylogone Ganodermophthora sp. nov., an ascomycetous pathogen causing yellow rot on cultivated mushroom Ganoderma lucidum in Korea. Mycologia 102 (5): 1167–1184. https://doi.org/10.3852/09-304
Katoh, K. & Standley, D.M. (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30 (4): 772–780. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst010
Minh, Q., Nguyen, M. & von Haeseler, A.A. (2013) Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30, 1188–1195. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst024
Nguyen, L.T., Schmidt, H.A., von Haeseler, A. & Minh, B.Q. (2015) IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Molecular Biology and Evolution 32, 268–274. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msu300
Ronquist, F., Teslenko, M., van der Mark, P., Ayres, D.L., Darling, A., Höhna, S., Larget, B., Liu, L., Suchard, M.A. & Huelsenbeck, J.P. (2012) MrBayes 3.2: e?cient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology 61, 539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
Sigler, L. & Carmichael, J.W. (1976) Taxonomy of Malbranchea and some other Hyphomycetes with arthroconidia. Mycotaxon 4: 349–488.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A. & Kumar, S. (2013) MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30: 2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tewari, R.P. & Macpherson, C.R. (1971) A new dimorphic fungus, Oidiodendron kalrae: morphological and biochemical characteristics. Mycologia 63: 602–611. https://doi.org/10.2307/3757556
Vilgalys, R. & Hester, M. (1990) Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. Journal of Bacteriology 172: 4238–4246. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.172.8.4238-4246.1990
Voigt, K. & Wöstemeyer, J. (2000) Reliable amplification of actin genes facilitates deep-level phylogeny. Microbiological Research 155: 179–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0944-5013(00)80031-2
White, T.J., Bruns, T., Lee, S. & Taylor, J. (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J. & White, T.J. (Eds.) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications, Academic Press, San Diego, California, pp 315–322.
Yoshitsugu, S. & Masaki, H. (2010) Arthrographis kalrae, a rare causal agent of onychomycosis, and its occurrence in natural and commercially available soils. Medical Mycology 48: 2, 384–389. https://doi.org/10.3109/13693780903219014
Zhang, D., Gao, F.L., Jakovli?, I., Zou, H., Zhang, J., Li, W.X. & Wang, G.T. (2020) PhyloSuite: an integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Molecular Ecology Resources 20 (1): 348–355. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.13096
Zhang, Z.Y., Dong, C.B., Chen, W.H., Mou, Q.R., Lu, X.X., Han, Y.F., Huang, J.Z. & Liang, Z.Q. (2020a) The enigmatic Thelebolaceae (Thelebolales, Leotiomycetes): one new genus Solomyces and five new species. Frontiers in Microbiology 11: 572596. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.572596
Zhang, Z.Y., Shao, Q.Y., Li, X., Chen, W.H., Liang, J.D., Han, Y.F., Huang, J.Z. & Liang, Z.Q. (2021) Culturable fungi from Urban soils in China I: description of 10 new taxa. Microbiology Spectrum 9: e00867–21. https://doi.org/10.1128/Spectrum.00867-21
Zhang, Z.Y., Zhao, Y.X., Shen, X., Chen, W.H., Han, Y.F., Huang, J.Z., Liang, Z.Q.(2020b) Molecular phylogeny and morphology of Cunninghamella guizhouensis sp. nov. (Cunninghamellaceae, Mucorales), from soil in Guizhou, China. Phytotaxa 455 (1): 31–39. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.455.1.4
Boana, P., Arthur, I., Golledge, C. & Ellis, D. (2012) Refractory Arthrographis kalrae native knee joint infection. Medical Mycology Case Reports 1 (1): 112–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mmcr.2012.10.005
Capella-Gutierrez, S., Silla-Martinez, J.M. & Gabaldon, T. (2009) TrimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 25: 1972–1973. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp348
Chen, C.J., Chen, H., Zhang, Y., Thomas, H.R., Frank, M.H., He, Y.H. & Xia, R. (2020) TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Molecular Plant 13 (8): 1194–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Chin-Hong, P.V., Sutton, D.A., Roemer, M., Jacobson, M.A. & Aberg, J.A. (2001) Invasive fungal sinusitis and meningitis due to Arthrographis kalrae in a patient with AIDS. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 39: 804–807. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.39.2.804-807.2001
Giraldo, A., Gené, J., Sutton, D.A., Madrid, H., Cano, J., Crous, P.W. & Guarro, J. (2014) Phylogenetic circumscription of Arthrographis (Eremomycetaceae, Dothideomycetes). Persoonia 32: 102–114. https://doi.org/10.3767/003158514x680207
Hernández-Restrepo, M., Giraldo, A., van Doorn, R., Wingfield, M.J., Groenewald, J.Z., Barreto, R.W., Colmán, A.A., Mansur, P.S.C. & Crous, P.W. (2020) The genera of Fungi – G6: Arthrographis, Kramasamuha, Melnikomyces, Thysanorea, and Verruconis. Fungal Systematics and Evolution 6 (1). https://doi.org/10.3114/fuse.2020.06.01
Kalyaanamoorthy, S., Minh, B.Q., Wong, T.K.F., von Haeseler, A. & Jermiin, L.S. (2017) ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nature Methods 14 (6): 587–589. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4285
Kang, H.J., Sigler, L., Lee, J., Gibas, C.F., Yun, S.H. & Lee, Y.W. (2010) Xylogone Ganodermophthora sp. nov., an ascomycetous pathogen causing yellow rot on cultivated mushroom Ganoderma lucidum in Korea. Mycologia 102 (5): 1167–1184. https://doi.org/10.3852/09-304
Katoh, K. & Standley, D.M. (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30 (4): 772–780. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst010
Minh, Q., Nguyen, M. & von Haeseler, A.A. (2013) Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30, 1188–1195. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst024
Nguyen, L.T., Schmidt, H.A., von Haeseler, A. & Minh, B.Q. (2015) IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Molecular Biology and Evolution 32, 268–274. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msu300
Ronquist, F., Teslenko, M., van der Mark, P., Ayres, D.L., Darling, A., Höhna, S., Larget, B., Liu, L., Suchard, M.A. & Huelsenbeck, J.P. (2012) MrBayes 3.2: e?cient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology 61, 539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
Sigler, L. & Carmichael, J.W. (1976) Taxonomy of Malbranchea and some other Hyphomycetes with arthroconidia. Mycotaxon 4: 349–488.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A. & Kumar, S. (2013) MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30: 2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tewari, R.P. & Macpherson, C.R. (1971) A new dimorphic fungus, Oidiodendron kalrae: morphological and biochemical characteristics. Mycologia 63: 602–611. https://doi.org/10.2307/3757556
Vilgalys, R. & Hester, M. (1990) Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. Journal of Bacteriology 172: 4238–4246. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.172.8.4238-4246.1990
Voigt, K. & Wöstemeyer, J. (2000) Reliable amplification of actin genes facilitates deep-level phylogeny. Microbiological Research 155: 179–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0944-5013(00)80031-2
White, T.J., Bruns, T., Lee, S. & Taylor, J. (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J. & White, T.J. (Eds.) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications, Academic Press, San Diego, California, pp 315–322.
Yoshitsugu, S. & Masaki, H. (2010) Arthrographis kalrae, a rare causal agent of onychomycosis, and its occurrence in natural and commercially available soils. Medical Mycology 48: 2, 384–389. https://doi.org/10.3109/13693780903219014
Zhang, D., Gao, F.L., Jakovli?, I., Zou, H., Zhang, J., Li, W.X. & Wang, G.T. (2020) PhyloSuite: an integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Molecular Ecology Resources 20 (1): 348–355. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.13096
Zhang, Z.Y., Dong, C.B., Chen, W.H., Mou, Q.R., Lu, X.X., Han, Y.F., Huang, J.Z. & Liang, Z.Q. (2020a) The enigmatic Thelebolaceae (Thelebolales, Leotiomycetes): one new genus Solomyces and five new species. Frontiers in Microbiology 11: 572596. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.572596
Zhang, Z.Y., Shao, Q.Y., Li, X., Chen, W.H., Liang, J.D., Han, Y.F., Huang, J.Z. & Liang, Z.Q. (2021) Culturable fungi from Urban soils in China I: description of 10 new taxa. Microbiology Spectrum 9: e00867–21. https://doi.org/10.1128/Spectrum.00867-21
Zhang, Z.Y., Zhao, Y.X., Shen, X., Chen, W.H., Han, Y.F., Huang, J.Z., Liang, Z.Q.(2020b) Molecular phylogeny and morphology of Cunninghamella guizhouensis sp. nov. (Cunninghamellaceae, Mucorales), from soil in Guizhou, China. Phytotaxa 455 (1): 31–39. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.455.1.4