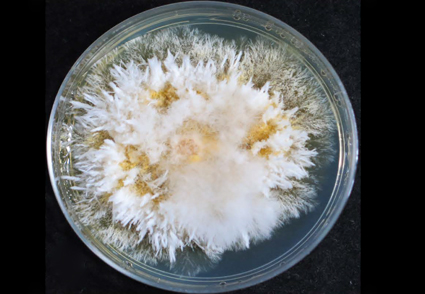
Abstract
During an investigation of fungicolous fungi associated with mushrooms in China, four boleticolous fungi were collected from Sichuan Province. Based on the morphological features and multi-gene phylogenetic analyses this study introduces two new species, Hypomyces ampullaris, and H. sichuanensis. The new species are described and illustrated comprehensively and compared with their related fungi. Hypomyces ampullaris is similar to Sepedonium ampullosporum in forming candelabrum-like conidiophores and producing ampulliform conidia but differs from the latter in having shorter phialides and smaller ampulloconidia. Hypomyces sichuanensis is similar to H. chrysospermus, H. microspermus, and Sepedonium laevigatum in forming poorly developed verticills conidiophores and the shape and size of aleurioconidia. However, the asexual spores of H. sichuanensis averaged somewhat smaller than those of H. chrysospermus and S. laevigatum, and larger than that of H. microspermus. Additionally, H. ampullaris and H. sichuanensis distinct from their close relatives in no pigment discoloration of the PDA medium. These species introduced here, improve our understanding of the diversity of Hypomyces, especially of the boleticolous Hypomyces in China.
References
Cunningham, C.W. (1997) Can three incongruence tests predict when data should be combined? Molecular Biology and Evolution 14 (7): 733–740. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a025813
Damon, S.C. (1952) Two noteworthy species of Sepedonium. Mycologia 44 (1): 86–96. https://doi.org/10.1080/00275514.1952.12024172
Dou, K., Lu, Z.X., Wu, Q., Ni, M., Yu, C.J., Wang, M., Li, Y. Q., Wang, X.H., Xie, H., Chen, J. & Zhang, C.H. (2020) MIST: A multiloci identification system for Trichoderma. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 86 (18): e01532-20 https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01532-20
Hyde, K.D., Norphanphoun, C., Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N., Bhat, D.J., Jones, E.B.G., Bundhun, D., Chen, Y.J., Bao, D.F., Boonmee, S., Calabon, M.S., Chaiwan, N., Chethana, K.W.T., Dai, D.Q., Dayarathne, M.C., Devadatha, B., Dissanayake, A.J., Dissanayake, L.S., Doilom, M., Dong, W., Fan, X.L., Goonasekara, I.D., Hongsanan, S., Huang, S.K., Jayawardena, R.S., Jeewon, R., Karunarathna, A., Konta, S., Kumar, V., Lin, C.G., Liu, J.K., Liu, N.G., Luangsaard, J., Lumyong, S., Luo, Z.L., Marasinghe, D.S., McKenzie, E.H.C., Niego, A.G.T., Niranjan, M., Perera, R.H., Phukhamsakda, C., Rathnayaka, A.R., Samarakoon, M.C., Samarakoon, S.M.B.C., Sarma, V.V., Senanayake, I.C., Shang, Q.J., Stadler, M., Tibpromma, S., Wanasinghe, D.N., Wei, D.P., Wijayawardene, N.N., Xiao, Y.P., Yang, J., Zeng, X.Y., Zhang, S.N. & Xiang, M.M. (2020) Refined families of Sordariomycetes. Mycosphere 11 (1): 305–1059. https://doi.org/10.5943/mycosphere/11/1/7
Katoh, K. & Standley, D.M. (2013) MAFFT Multiple sequence alignment software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30 (4): 772–780. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst010
Nylander, J.A.A. (2004) MrModeltest v2. Program distributed by the author. Available from: https://github.com/nylander/MrModeltest2 (accessed 19 August 2021)
Poldmaa, K. (2000) Generic delimitation of the fungicolous Hypocreaceae. Studies in Mycology 45: 83–94.
Poldmaa, K. (2011) Tropical species of Cladobotryum and Hypomyces producing red pigments. Studies in Mycology 68: 1–34. https://doi.org/10.3114/sim.2011.68.01
Poldmaa, K. & Samuels, G.J. (1999) Aphyllophoricolous species of Hypomyces with KOH negative perithecia. Mycologia 91 (1): 177–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/00275514.1999.12061007
Poldmaa, K. & Samuels, G.J. (2004) Fungicolous hypocreaceae (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) from Khao Yai National Park, Thailand. Sydowia 56 (1): 79–130.
Rehner, S.A. & Samuels G.J. (1994) Taxonomy and phylogeny of gliocladium analyzed from nuclear large subunit sibosomal DNA sequences. Mycological Research 98: 625–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0953-7562(09)80409-7
Rogerson, C.T. & Samuels, G.J. (1985) Species of Hypomyces and Nectria occurring on Discomycetes. Mycologia 77 (5): 763–783. https://doi.org/10.1080/00275514.1985.12025164
Rogerson, C.T. & Samuels, G.J. (1989) Boleticolous species of Hypomyces. Mycologia 81 (3): 413–432. https://doi.org/10.1080/00275514.1989.12025764
Rogerson, C.T. & Samuels, G.J. (1993) Polyporicolous Species of Hypomyces. Mycologia 85 (2): 231– 272. https://doi.org/10.1080/00275514.1992.12026272
Rogerson, C.T. & Samuels, G.J. (1994) Agaricicolous species of Hypomyces. Mycologia 86 (6): 839–866. https://doi.org/10.1080/00275514.1994.12026489
Ronquist, F., Teslenko, M., van der Mark, P., Ayres, D.L., Darling, A., Hohna, S., Larget, B., Liu, L., Suchard, M.A. & Huelsenbeck, J.P. (2012) MrBayes 3.2: efficient bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology 61 (3): 539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
Rossman, A.Y., Seifert, K.A., Samuels, G.J., Minnis, A.M., Schroers, H.J., Lombard, L., Crous, P.W., Poldmaa, K., Cannon, P.F., Summerbell, R.C., Geiser, D.M., Zhuang, W.Y., Hirooka, Y., Herrera, C., Salgado-Salazar C. & Chaverri P. (2013) Genera in Bionectriaceae, Hypocreaceae, and Nectriaceae (Hypocreales) proposed for acceptance or rejection. IMA Fungus 4 (1): 41–51. https://doi.org/10.5598/imafungus.2013.04.01.05
Sahr, T., Ammer, H., Besl H. & Fischer M. (1999) Infrageneric classification of the boleticolous genus Sepedonium: species delimitation and phylogenetic relationships. Mycologia 91 (6): 935–943. https://doi.org/10.1080/00275514.1999.12061104
Stamatakis, A. (2006) RAxML–VI–HPC: Maximum likelihood based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22 (21): 2688–2690. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btl446
Sun, J.Z., Liu, X.Z., Jeewon, R., Li, Y.L., Lin, C.G., Tian, Q., Zhao, Q., Xiao, X.P., Hyde, K.D. & Nilthong S. (2019a) Fifteen fungicolous Ascomycetes on edible and medicinal mushrooms in China and Thailand. Asian Journal of Mycology 2 (2): 129–169. https://doi.org/10.5943/ajom/2/1/7
Sun, J.Z., Liu, X.Z., McKenzie, E.H.C., Jeewon, R., Liu, J.K., Zhang, X.L., Zhao, Q. & Hyde K.D. (2019b) Fungicolous fungi: terminology, diversity, distribution, evolution, and species checklist. Fungal Diversity 95 (1): 337–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-019-00424-7.
Tamm, H. &Poldmaa, K. (2013) Diversity, host associations, and phylogeography of temperate aurofusarin producing Hypomyces/Cladobotryum including causal agents of cobweb disease of cultivated mushrooms. Fungal Biology 117 (5): 348–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funbio.2013.03.005
Valdez, G.U. & Douhan, G.W. (2012) Geographic structure of a bolete infecting cryptic species within the Hypomyces microspermus species complex in California. Mycologia 104 (1): 14–21. https://doi.org/10.3852/09-272
Wijayawardene, N.N., Hyde, K.D., Tibpromma, S., Wanasinghe, D.N., Thambugala, K.M., Tian, Q., Wang, Y. & Fu, L. (2017) Towards incorporating asexual fungi in a natural classification: checklist and notes 2012-2016. Mycosphere 8 (9): 1457–1555. https://doi.org/10.5943/mycosphere/8/9/10
Zare, R. & Gams, W. (2016) More white verticillium-like anamorphs with erect conidiophores. Mycological Progress 15: 993–1030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-016-1214-8
Zeng, Z.Q. & Zhuang, W.Y. (2015) Current understanding of the genus Hypomyces (Hypocreales). Mycosystema 34: 809–816. https://doi.org/10.13346/j.mycosystema.140116
Zeng, Z.Q. & Zhuang, W.Y. (2016) Three new species and two new Chinese records of Hypomyces (Hypocreales). Mycosystema 35: 1048–1055. https://doi.org/10.13346/j.mycosystema.160105
Zeng, Z.Q. & Zhuang, W.Y. (2019) Two New Species and a new chinese record of hypocreaceae as evidenced by morphological and molecular data. Mycobiology 47 (3): 280–291. https://doi.org/10.1080/12298093.2019.1641062
Zhang, J.J., Kapli, P., Pavlidis, P. & Stamatakis, A.A (2013) General species delimitation method with applications to phylogenetic placements. Bioinformatics 29: 2869–2876. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt499